- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
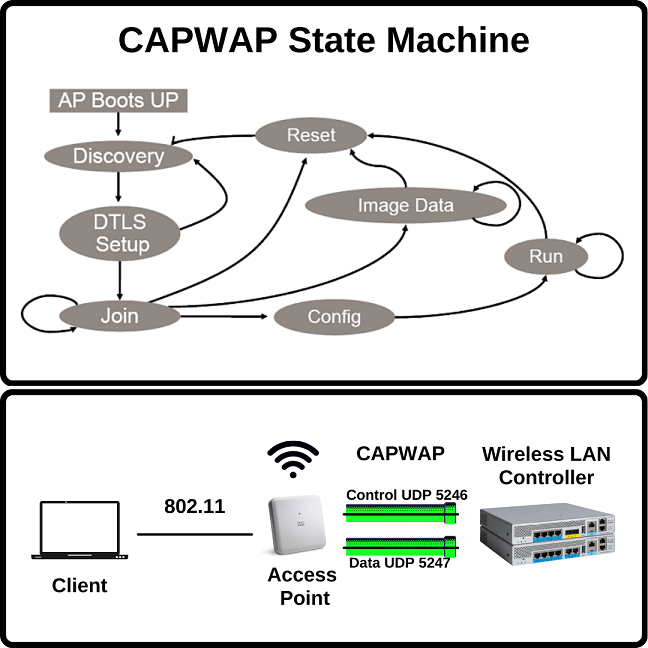
Table of Contents
In this lesson, we will focus on a wireless tunnel protocol, CAPWAP (Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points). We will answer what is CAPWAP question detailly. CAPWAP Protocol is a standard networking protocol with which WLCs can manage a group of Access Points. In such a topology, every Access Point is connected to the Wireless LAN Controller with a CAPWAP Tunnel and all the traffic is sent through this CAPWAP Tunnel. For detailed information about CAPWAP, you can also check RFC 4347, RFC 4564, RFC 5415 and RFC 5418.For Access Point Discovery and Join Process overview, you can check the releated lesson.
CAPWAP versus LWAPP: Comparison
CAPWAP was developed by IETF at 2009. It is based on LWAPP. There are three aims of IETF for CAPWAP protocol development. These are given below:
With the help of CAPWAP, WLCs can manage configurations and hardware of multiple nodes. By doing this, it provides a proper network. It also prevents the network towards any rogue devices.
CAPWAP do not support layer 2 mode. But LWAPP supports both layer 2 mode and layer3 mode.
Wireless Access Points need to be joined to a WLC. To do this, it needs AP Discovery process and WLC Join process. For the Discovery process, AP sends a Discovery request message. Any WLC in the network responds this with a Discovery response message. After that a secure connection with DTLS is established between these two ends. DTLS is the abbreviation of Datagram Transport Layer Security.
After discovery process, CAPWAP Join process is done. For this AP sends CAPWAP Join Request. CAPWAP Join Request Message includes some information about AP. These are given below:
As a response, WLC sends a CAPWAP Join Response. CAPWAP Join Response Message includes some more information about Wireless LAN Controller. These are given below:
There are two CAPWAP messages sent over this connection. Data messages and Control messages. Data messages are the encapsulated messages which is forwarded from or to wireless clients. Data messages use UDP port 5247. Control messages are the WLAN management messages that are used between Access Point and WLC. Control messages use UDP port 5246.
CAPWAP supports two operation modes. These are Split MAC Mode and Local MAC Mode. In Split MAC Mode, all layer 2 management and data frames are encapsulated between WLC and AP. In Local MAC Mode, data frames are locally tunneled.
Below, you can find CAPWAP State Machine. This diagram is important to show you the CAPWAP steps after AP boots up. This diagram will help you during your troubleshooting activities a lot.
There are various CAPWAP commands are used to configure CAPWAP and manage it. These commands are given below:
capwap ap To configure the primary, secondary & tertiary controllers for the AP
capwap ap hostname To configure AP hostname
capwap ap ip To configure static IP address and DNS for AP
capwap ap mode To configure AP mode
capwap ap auth-token To configure authentication token for AP
capwap ap ethernet To configure AP Ethernet parameters
capwap ap ethernet tag 2 To configure Ethernet VLAN tagging on the AP
capwap ap lag To configure CAPWAP lag
capwap ap restart To restart the CAPWAP protocol
capwap ap erase all To erase CAPWAP configuration
You can also check LWAPP Protocol and Access Point Discovery and Join Process to learn related lessons about CAPWAP.
Leave a Reply