- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
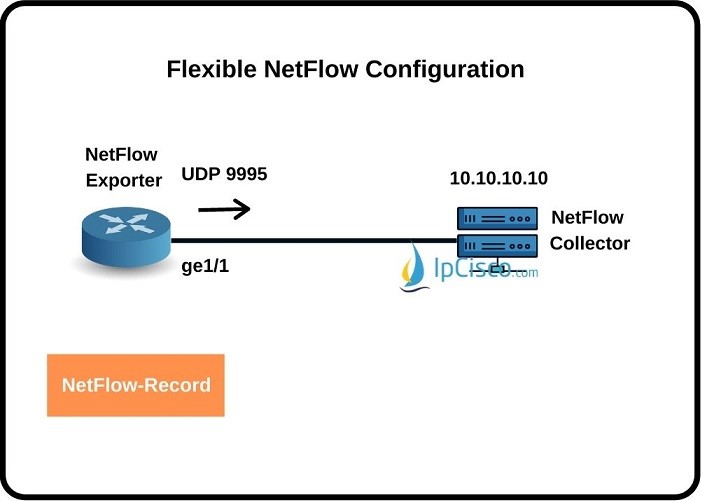
In this lesson, we will learn how to configure Flexible Netflow on Cisco Routers. We will see Cisco Flexible Netflow Configuration steps one by one with a configuration example. Before, we have also see Traditional NetFlow Configuration on Cisco Routers.
To configure Flexible Netflow Cisco, we will use five main steps. These steps and the commands that we will use in these steps are given below:
Here, according to Flow Exporter and Sampler usage, the configuration can change.
Now, let’s see each of these steps and the related Flexible Netflow Configuration Commands.
Table of Contents
In this first step, we will create Flow Record with “flow record” command. Then we will add matching traffic and then we will mention the collect information. We will use Netflow-record as flow record name.
Router(config) # flow record Netflow-Record
Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 tos
Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 protocol
Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 source address
Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 destination address
Router(config-flow-record) # match transport source-port
Router(config-flow-record) # match transport destination-port
Router(config-flow-record) # match interface input
Router(config-flow-record) # collect interface output
Router(config-flow-record) # collect counter bytes
Router(config-flow-record) # collect counter packets
Router(config-flow-record) # exit
In the second step, we will configure Flow Exporter. Here, as a destination, we will give the Flow Collector’s IP address and we will set source port.
The configuration commands that we will use will be like below:
Router(config)# flow exporter exporter-name
Router(config-flow-exporter)# destination {hostname | ip-address}
Router(config-flow-exporter) # source source-port
Router(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp udp-port
For our example, Netflow Exporter ip address will be 10.10.10.10. Oour source port will be ge1/1 and we will use the UDP port 9995. our configuration will be like below:
Router(config) # flow exporter Netflow-Exporter
Router(config-flow-exporter) # destination 10.10.10.10
Router(config-flow-exporter) # source ge1/1
Router(config-flow-exporter) # transport udp 9995
Router(config-flow-exporter) # exit
In this step, firstly, we will create sampler with “sampler sampler-name” command. And then, we will determine the mode and sample number for window size.
Router(config) # sampler SamplerXYZ
Router(config-sampler) # mode {deterministic | random} 1 out-of window-size
router(config-sampler)# end
This is not a requirement but if we need to avoid traffic performance problem for high traffic, we can use Flow Sampler and limit number of monitored packets.
In this step, we will configure Flow Monitor. We will take from one side and record to another side. We will also mention cache time out.
router(config-flow-exporter)# flow monitor flow-monitor-name
router(config-flow-monitor)# exporter exporter-name
Router(config-flow-monitor) # record record-name
Router(config-flow-monitor) # cache timeout active timeout-time
router(config-flow-monitor)# end
For our example, we will use Netflow-Montor as Flow monitor name and we will use Netflow-record as record name. Our cache timeout will be 60.
Router(config) # flow monitor Netflow-Monitor
Router(config-flow-monitor) # exporter Netflow-Exporter
Router(config-flow-monitor) # record Netflow-Record
Router(config-flow-monitor) # cache timeout active 60
Router(config-flow-monitor) # exit
In the last step, we will apply this Flow Monitor to the interface both input and output direction. We will apply Netflow-Monitor as Netflow Monitor to interface fa0/0 through both input and output direction.
Router(config) # interface fa0/0
Router(config-if) # ip flow monitor Netflow-Monitor input
Router(config-if) # ip flow monitor Netflow-Monitor output
Router(config-if) # exit
Leave a Reply