- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
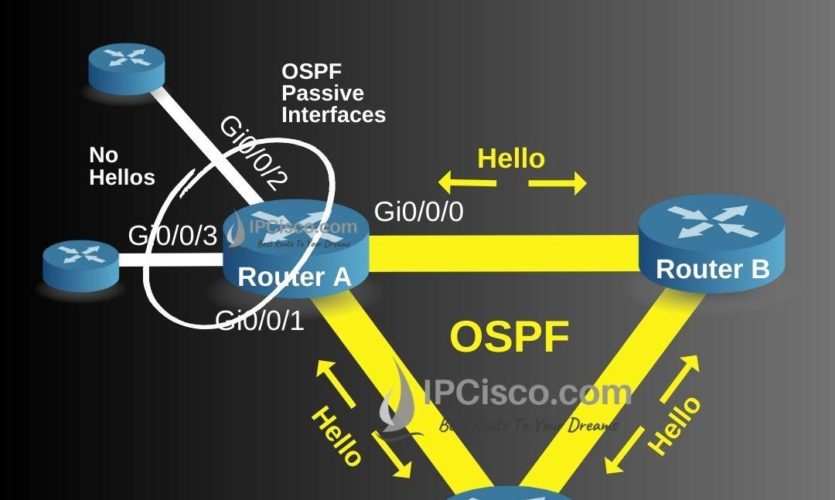
Table of Contents
Routing protocols establish neighborships with the connected routers and they talk each other about routing updates. OSPF is a Link-State routing protocol which also uses Hello packets. Normally, on each interface these Hello packets are sent and received. But with OSPF Passive Interface configuration, we can prevent this. After this configuration, Hello packets is not sent through that the passive interface.
This method is not only used in OSPF networks but it is also used in EIGRP networks too.
Here, connected network is still advertised by OSPF network. Here, Hello packets are not sent to or received from this interface.
Why we use OSPF Passive Interface? We use passive interfaces on the interfaces which do not need to communicate with routing protocol. By doing this we can reduce the overhead over the router. Because, more Hellos means more overhead and CPU usage.
Beside this, using passive interface in OSPF provide more security. A malicious user can manipulate Hello packets from a device and sent it to the OSPF network. This can damage your OSPF network. To prevent this, we prevent getting Hellos from unnecessary interfaces.
DOWNLOAD Cisco Packet Tracer Configuration Examples and Cisco GNS3 Labs!
We have learned what is passive interfaces in OSPF and why we use it. Now, let’s configure OSPF Passive interface on Cisco router. We will use the below network topology for our example.
To do this, we will use “passive-interface interface-name” command. We will use this command under OSPF process to specift the passive interfaces with their interface names.
Router A# configure terminal
Router A(config)# router ospf 1
Router A(config-router)# passive-interface Gi0/0/2
Router A(config-router)# passive-interface Gi0/0/3
If we have many more interfaces that need to be passive, then we can set all the interfaces as passive interface and then open Hello communication on specific interfaces. To set all the interfaces as passive interface, we will use “passive-interface default” command. Then, we will allow specific interfaces by removing its passive status with “no passive-interface interface-name” command.
Router A(config)# router ospf 1
Router A(config-router)# passive-interface default
Router A(config-router)# no passive-interface gi0/0/0
Router A(config-router)# no passive-interface gi0/0/1
To verify passive interface configuration in OSPF, we can use “show ip ospf interface” command.
Router A# show ip ospf interface
….
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 172.16.0.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 5.5.5.5, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
GigabitEthernet0/0/3 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 192.168.0.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 5.5.5.5, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
We have completed our OSPF configuration example. You will use this configuration in your OSPF job operations.
DOWNLOAD Cisco Packet Tracer Configuration Examples and Cisco GNS3 Labs!
Leave a Reply