- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
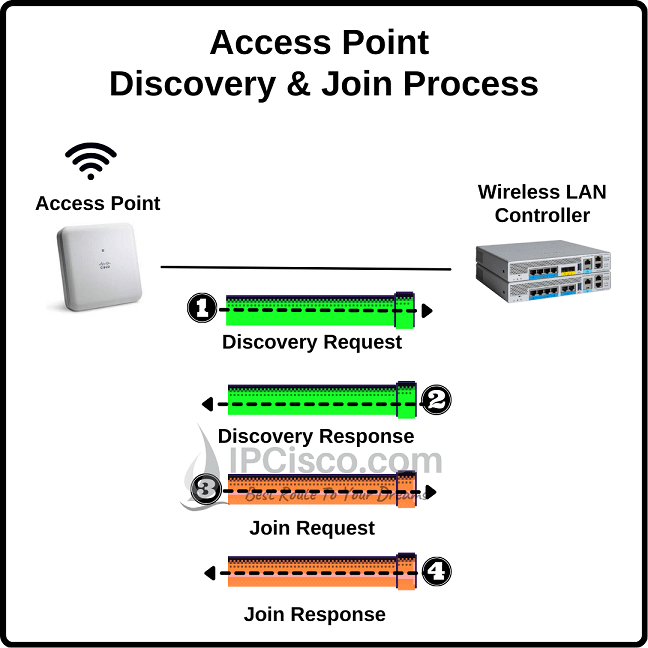
Access Points can be managed by Wireless LAN Controller. To manage an Access Point with a WLC, Access Point must be joined to a WLC. Access Point must complete two phases to join to a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). In this lesson we will cover Access Point Discovery and Join Process.
For Access Point Discovery and Join Process, these are tew process. These are given below:
Basically, in Discovery Process, AP finds a WLC. And in Join Process, AP joins to the WLC.

For Discovery and Join Phases, two different protocols can be used. These protocols are:
CAPWAP versus LWAPP: Comparison
To learn more on CAPWAP and LWAPP, you can check the related CAPWAP and LWAPP lessons. You can also check CAPWAP vs LWAPP comparison lesson for the detailed differences of these two wireless tunnelling protocols.
There are common steps for Access Point Registration Process. Let’s talk about these steps one by one for CAPWAP.
Table of Contents
AP must discover and then join to the WLC to be managed by WLC. For this process, two phases are used as we have talked about briefly before. Now, let’s briefly see the steps of this process.
Now, let’s learn more on these two phases and the details of Access Point Discovery and Join Process.
To join a WLC, firstly, Access Point needs to discover this WLC. In other words, it must find an available WLC and it must know something about the WLC that it will join. This is AP Discovery Phase. So, how can an Access Point discover a WLC?
There are different ways for AP Discovery Phases. In other words, there are multiple ways for an AP to discover a WLC. These are given below:
The first method is sending a broadcast message on local subnet. To do this, Access Point sends a broadcast CAPWAP Discovery message on UDP 5246 port. If are there any WLC on the subnet, they reply with a unicast discovery response. With this message WLC Discovery Phase is achieved.
If there are WLCs outside of your network, you can use ip helper functionality to discover the WLCs outside of your network. This is similar to DHCP Relay Agent logic.
Router (config)# interface a/b/c
Router (config-if)# ip helper-address WLC-Management-IP
You can learn also FTP Port and other Network Ports on related lessons.
Access Points can store last 8 Wireless LAN Controllers to which it had joined before. An AP can check these WLC IP addresses to send a new join request again. This is the second way for WLC Discovery Phase.
If a DHCP is used for Access Point, some additional parameters can be passed from DHCP Server to the Access Point with options. One of these options is DHCP Option 43. DHCP Option 43 can be used to discover a Wireless LAN Controller. DHCP Option 43 includes the management IP address of one or more WLCs that can be used by Access Point.
For WLC Discovery Phase, the other way is using DNS. To do this, there must be a DNS server configured in Access Point or a DNS service offered by DHCP Server or there must be a DNS Server on the network. If one of these DNS services exist, Access Point can resolve DNS records related with CAPWAP or LWAPP Controller.
The last way for WLC Discovery Phase is manual configuration. Sometimes, WLC IP address can be configured manually on the Access Point (AP). When there is a manual WLC IP Configuration on AP, AP uses this WLC address.
Router (config)# capwap ap ip address ip-address subnet-mask
Router (config)# capwap ap ip default-gateway ip-address
Router (config)# capwap ap controller ip address ip-address
With WLC Discovery Phase, Access Point finds at least one WLC to join. After completing WLC Discovery Phase, now, it is time to AP Join Phase. It builds an encrypted tunnel between AP-Manager and AP. To do this, CAPWAP Join Request and CAPWAP Join Response messages are used.
Access Point can find one or more Wireless LAN Controllers to join. Then, which WLC does AP decide to join and how?
AP firstly selects the old WLCs that it had joined before. Or it selects a WLC which can be configured as primary, secondary etc. WLC on the system.
Secondly, AP select the WLC which is configured as Master Controller on the network.
Lastly, Access Point select the one which has the lowest number of APs on it. In other words, it selects the lowest loaded WLC.
To connect a WLC, Access Point needs to complete some more steps after Access Point Discovery and Join Process. These steps are given below:
Firstly, AP checked the image if are there any mismatch between AP and WLC. If are there any, it downloads image and loads it. Again, AP checks the configuration on WLC and if are there any update, it downloads the latest configuration. Lastly, the registration is done.
We have talked about the details of Access Point Discovery and Join Process. For more information abut related protocols like LWAPP and CAPWAP, you can check the related lessons.
Leave a Reply