- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
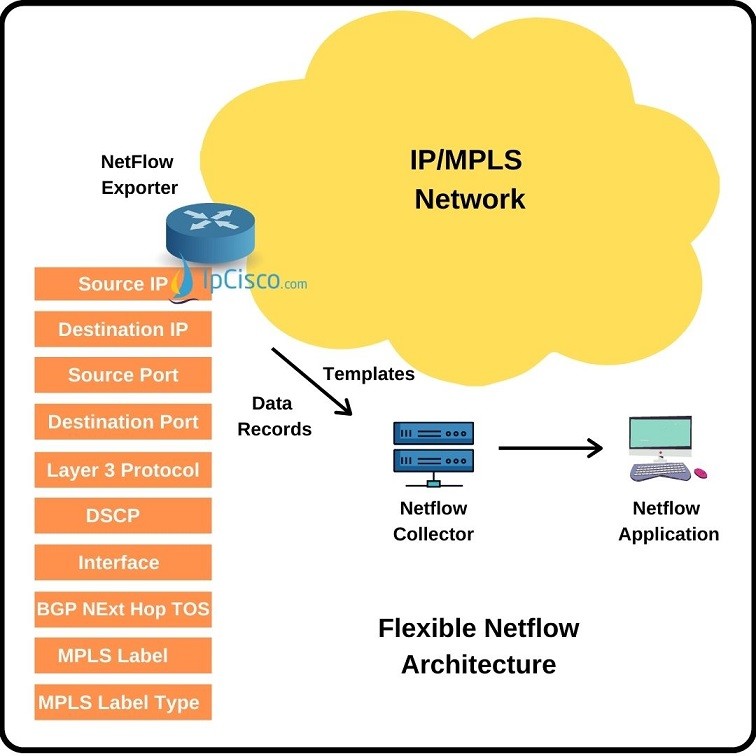
Table of Contents
NetFlow is a protocol developed by Cisco to monitor and analyze network traffic flows. And now there is an enhanced version. This is Flexible NetFlow. Basically, Flexible NetFlow is an extension of Traditional NetFlow. In other words, it is advanced and next generation NetFlow technology. In another lesson, we will see How to Configure Flexible Netflow on Cisco Routers.
Flexible NetFlow is Cisco ‘s one of the Next Generation Technologies that provides detailed analyze and more information than the previous version. Flexible Netflow provides the ability to monitor a wide range of packet information as expansion of Traditional Netflow. It uses Deep Packet Inspection to achieve this.
So, what is Deep Packet Inspection?
Deep Packet Inspection or shortly DPI is basically a network packet filtering. It is an advanced method of managing network traffic. DPI is a method that inspects not only the packet’s multiple headers, but also the data content of the packet. So, you can learn the network traffic deeply. You can identify different application data like youtube, facebook, Skype etc.

Especially in the Packet Core Networks of Mobile Operators, Deep Packet Inspection is very important. Here, with DPI, the user traffic is analyzed and classified. So, a specific policy can be used for a specific traffic. For example, only facebook traffic or youtube traffic of the users can be blocked or the speed of the data transfers of these applications can be limited.
In traditional Netflow, the flow analyze is not too much detailed. With Flexible Netflow and Deep Packet Inspection, the traffic flow analyze can be done detailly. Even the application traffics can be classified with Deep Packet Inspection.
With Deep Packet Inspection, different layer data can be anazled from layer 2 to layer 7. For this analze Cisco NBAR is also used together.
Another difference between Traditional Netflow and Flexible Netflow is about cache usage. Traditional Netflow uses one cache for all the tracked information. But Flexible Netflow uses different caches for different purposes. For example, billing information can use a cache and security analyze information can use another. Both of this traffic analyzes can be done simultaneously.
Beside Flexible Netflow can export interface data like name, descriptions etc. and this eliminates the usage of SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol).
Another difference is about additional tracking information. Flexible Netflow allows additional IP information in IPv4, IPv6 header fields, TCP flags etc. For security and malicious behavior analyze, this is very important.
In Flexible Netflow, there are three types of flows. In Traditional Netflow, there was only one flow. So, what are these Flexible Netflow flows? These are:
The Normal Cache is the same as in Traditional Netflow. Normal Cache uses flow timers to expire/age flows and export to the Netflow Collector.
The Permanent Cache is a configurable cache that helps accounting and security monitoring.
The Immediate Cache, allows end user to export a flow on demand.
There are different Netflow Components. These are:
Flows are defined by different flow information. These are called Flow Records. The parameters used to define a flow are given below:
The traffic that has the same parameters are defined as flow. These parameters can also used to define more specific flows.
Flow Monitors are the components used to monitor network traffic. They are applied to interfaces. After this application, a flow monitor cache is created. There are different modes of flow monitor cache can be used with each flow. These flow monitor cache modes are given below:
Layer 3 mode is the default mode. In this mode the cache entries are aged out according to the timeout parameters.
Immediate mode is the mode with which the cache entries are aged out immediately when they are created. We use this mode for the traffic information is needed immediately at the other end.
Permanent mode is the mode with which the newer cache entries are aged out. This mode is used when we need long term statistics on the device and for low number flow.
The flow data must be transferred for analyze. Flow Exporter is used for the transfer of Netflow Cache from the source to the remote system. There can be multiple Flow Exporters.
There can be a high traffic to analyze and this can affect the performance of the monitored device. To avoid this performance problem, Flow Sampler is used to limit the number of monitored packets by the Flow Monitor.
We can use Flexible Netflow for multiple aims. First of all we can use this next generation flow technology for a detailed flow analyze and Deep Packet Inspection (DPI). We can determine the usage behaviors of the network, different types of applications used in network and the details of this traffic.
To improve the network, we can use Flexible Netflow too. By measuring the productivity and the utilization of the network resources, we can determine the new steps. We can also determine the new impacts to the network.
As a security mechanism, we can determine the malicious attacks to our network. By determining the vulnerabilities of the network and analyzing the packets coming to network, we can prevent malicious behaviors.
We can understand the answers of the questions who, what, when, where and how questions about the network flow.
There are many benefits of Flexible Netflow. Some of these benefits are given below:
Leave a Reply