- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
IP addressing is one of the key lessons of networking. We use IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses on our networks for layer 3. There are different ip address types and in this lesson, we will focus on one of these ip address types. Here, we will focus Private ip addresses, in other words, we will learn the details of Private ip address ranges for both IPv4 and IPv6. We will also give private ip address examples for them.
Table of Contents
Private ip addresses are the ip address which are used on only local networks. Private ip ranges cannot be used on Internet. They are local ip addresses which can be used millions of times in different local networks. These addresses do not need to be unique in the world. They are not like unique Public ip addresses. They are the ip addresses assigned to our PC from our local DHCP Server. With NAT, we can use these ip addresses to go through internet. With NAT, private range ip addresses is translated to a public IP assigned by your Internet Service Provider.
When we talk about private ip addresses, we mean IPv4 private ip ranges. But there are also private ip address range for IPv6. And IPv6 private addresses are called IPv6 Unique Local Addresses. Like IPv4 private IP addresses, IPv6 Unique Local Addresses can not be used on Internet too.
You can also check Subnetting Examples Lesson and Subnetting Cheat Sheet!
There are different private ip address ranges used in networking. These private range addresses are used in local networks. They are not routable on Internet.
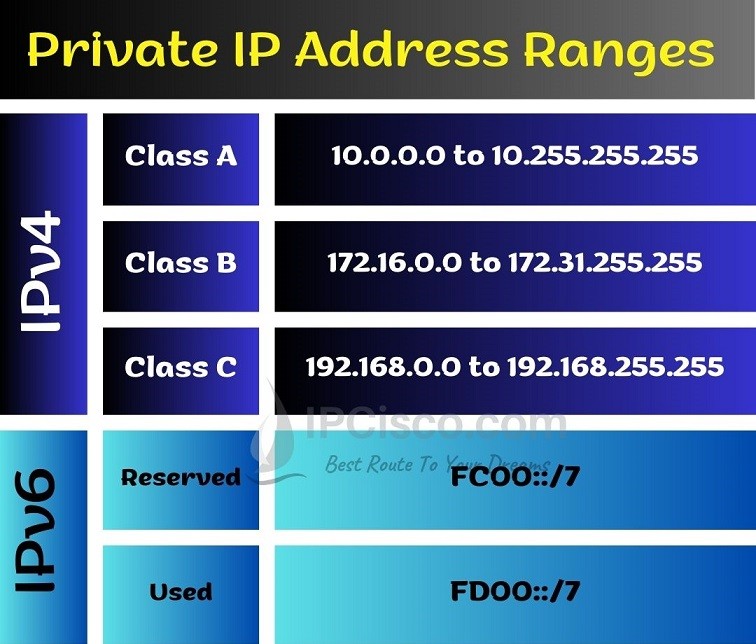
There are three IPv4 private ranges for Class A, Class B and Class C ip address ranges. These private ip address ranges are given below:
Class A range has 8 network bits and 24 host bits.
Class B range has 16 network bits and 16 host bits.
Class C range has 24 network bits and 8 host bits.
Like IPv4, IPv6 has also private IP address ranges. They are not routable addresses and so, we can not use these ranges on Internet too. To use these addresses on Internet, you need IPv6 NAT. Unique local addresses are used for local communication.
So, what are IPv6 private address ranges? Here there are two IPv6 private address ranges. These are given below:
FC00::/7 is the reserved IPv6 private address range by IANA.
FD00::/7 is the used IPv6 private range now.
Both. Do not mixed your mind with the question, “which one is Unique Local address range, FC00::/7 or FD00::/7?”. Both of them are private ipv6 address range but one of them is reserved for future use.
IPv6 Unique Local Addresses has 7 fixed bits at the beginning. But 8. Bit can change. This 8. Bit shows that if the address is locally assigned or it is reserved.
Now, let ‘s give some examples to private ip addresses. Firstly, let’s give a couple of example to different IPv4 private ip address ranges. You can increase these private ip address examples.
Now, let’s give private ip address examples for IPv6. In other words, let ‘s write IPv6 Unique local address examples:
169.254.0.1-169.254.255.254 ip range is the ip range used by operating systems to assign ip address automatically. If you have no manual ip address configuration and your DHCP server is unavailable, then operating system assigns an ip address to your device. These ip addressing is called APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing). These ip address range is not the ip address range that oyu will use your regular network operation.
To learn your Private IP address, you can check it with different commands on different operating systems.
If you are using Windows, you can use “ipconfig” command to display your private ip address and the other ip parameters.
If you are using Linux, you can use “ifconfig” command to display your private ip address and the other ip parameters.
Lastly, if your device is running MacOS for example if it is an IPhone or IPAD, you can go to settings, then click Wi-Fi. And, click the your network’s name. You will find your private ip address and other ip parameters there.
To learn our public IP address, in other words, to learn our global IP address assigned by your service provider, we will use a well-known website, Whatismyipaddress.
When you open this website, it will give you your Public IPv4 and IPv6 Addresses.
IP addresses are managed by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) in the world. IANA assigns these number to RIRs (Regional Internet Registries). And RIRs assign these ranges to the Companies or Service Providers. Lastly, service providers give these ip addresses to you. This is for Public IPv4 addresses or IPv6 Global Unicast addresses.
You can use any of IPv6 private ip addresses or IPv6 Unique local addresses in your local network. They are not unique in the world. Any device in the world can use any of these private ip address ranges.
Question 1: Which one is NOT one of the Private IP Address Ranges?
a) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
b) 224.0.0.0 to 234.168.255.255
c) 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
d) 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Question 2: Fill in the blanks: Class B range has … network bits and … host bits.
a) 8/8
b) 16/8
c) 16/32
d) 4/16
e) 16/16
Question 3: What is the range of APIPA?
a) 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
b) 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
c) 169.254.0.1-169.254.255.254
d) 224.0.0.0 to 234.168.255.255
e) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Question 4: Which ipv4 address classes are used for private ip address range? (Select 3)
a) Class A
b) Class B
c) Class C
d) Class D
e) Class E
Question 5: How many available addresses are there for a Class C Private IP Range?
a) 65.536
a) 1.048.576
c) 16.777.216
Answers: 1)b 2)e 3)c 4)a,b,c 5)a
Leave a Reply