- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is the second STP type. It is a fast converged version of Spanning Tree Protocol as its name implies. RSTP bypass the Blocking State and Listenning State of STP, and provide Forwarding State in 15 Seconds. So, the convergence time is lower than STP.
In some cases, Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol is similar to STP. But with some additional improvements, It is more useful. Let’s check the details. Youn can learn how to configure RSTP, on RSTP Configuration lessons.
Table of Contents
RSTP has port roles like STP. These Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Port Roles are:
Root Port is the port on a switch that is the closest way (Lowest Cost) to the Root Bridge.
Designated Port is the port, that can send the best BPDU on its segment.
Alternate Port is a blocking port that receives better BPDU from another switch. It is the backup of Root Port.
Backup Port is a blocking port that receives better BPDU from the same switch. It is the backup of Designated Port.
STP Algorithm determines the role of a port based on BPDUs. STP BPDU was using two bits of BPDU part. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol uses all eight bits. RSTP (802.1w) BPDU is given below:
Here, there is an additional port definion called “Edge Port”. Edge Ports are the ports that connect to the Host devices like PCs, Servers, etc. So, Edge Ports are not participate in RSTP calculation. They do not receive BPDUs and they can go to the Forwarding State immediately.
STP use two type of BPDU, RSTP use single type BPDU. Contains additional parameters to support the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol characteristics.
You can also view the related RFC 4318.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol has three states. These are:
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol bypasses the two states of STP. It bypasses Blocking State, Listenning State of STP. So, after the Discarding State, it goes to Forwarding State immediately. You can check the below STP and RSTP State comparison table.
RSTP Operation is similar to STP. Like STP, in RSTP, Root Bridge is selected firstly. Then port roles are determined. In Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol there are two additional port roles.
Firtly Root or Designated Ports are selected. Then, if a port is not selected as Root or Designated Port, that port becomes;
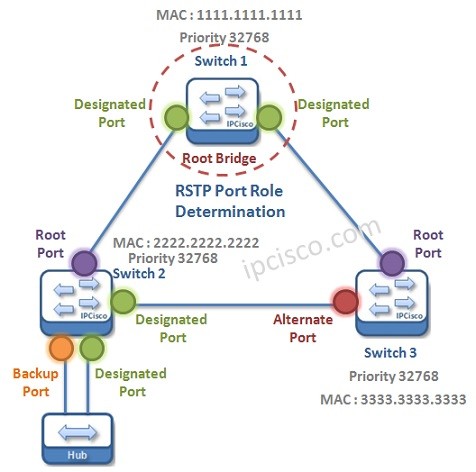
As an example, think about the below RSTP Topology. In this topology, there are three Switches and a Hub. Let’s determine the port roles for this Topology.
Here, the port of the Root Bridge will be Designated and the lowest cost port to the Root Bridge on other switches will be Root Port.
In Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, two different blocking port is determined as we mentined above. Here the blocking port on other swicth than the designated port will be selected as Alternate Port. And the blocking port in the same switch or segment, will be selected as Backup Port.

Lastly let’s mention, the interoparability of RSTP and STP. In different networks, these protocols can work together.
RSTP and STP are the similar two protocols. In your network, there can be switches that support both of these layer 2 protocol. But what if one switch in the network do not support Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol? The answer is easy. The Layer 2 topology works with STP only.
Leave a Reply