- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this lesson, we will focus on a network protocol which is important for network time synchronization. Here, we will learn What is PTP (Precision Time Protocol)? How we use it and How to Configure PTP on Cisco devices. Before we have learned similar NTP (Network Time Protocol) and How to Configure NTP on Cisco Routers. Here, our focus will be PTP (Precision Time Protocol).
Table of Contents
PTP is the abbreviation of Precision Time Protocol. It is a standard based network protocol defined as IEEE-1588 standard. PTP (Precision Time Protocol) is basically used for the clock synchronization throughout a computer network.
PTP clock accuracy is in the sub-microsecond range. This is a very good clock quality. PTP accuracy is higher than NTP (Network Time Protocol) accuracy. Because NTP provides only millisecond accuracy. This accuracy let Precision Time Protocol used in critical systems like financial transactions, aircraft monitoring.
PTP works with master slave architecture. There is a hierarchy between the clock sources in PTP network.
To test your networking knowledge, you can visit our All NEtwork Quizes Page!
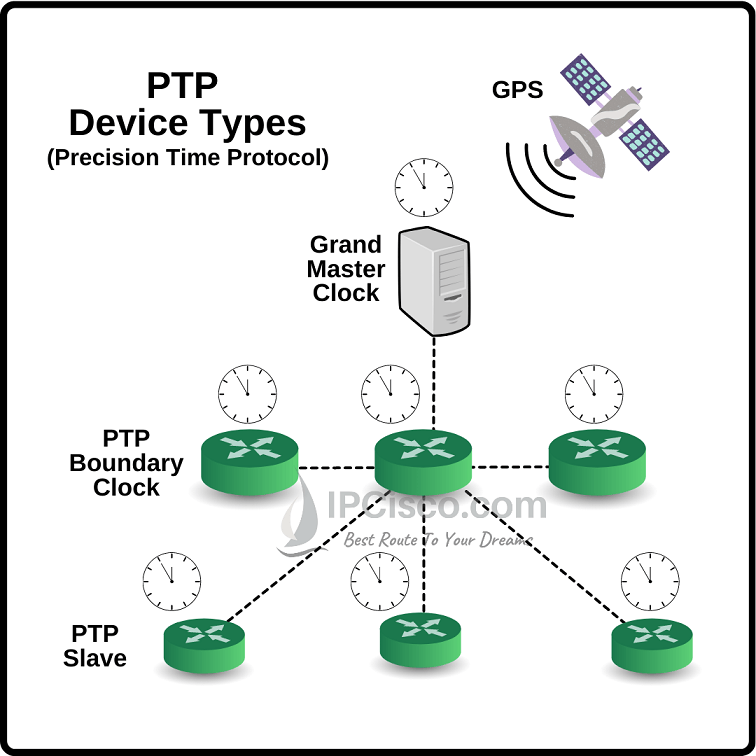
In a PTP network, there are different PTP clocks. With these PTP clocks, there is a hierarchical structure between different clocks. So, what are these PTP Clocks? These are given below:
Grandsource Clock (Primary Clock) is the primary source for clock. The criteria which make this clock Grandsource clock is the quality of the clock. This clock can be directly connected to the reference clock.
Boundary Clock is the local PTP clock. It is both a source and a client. It synchronizes itself with the upstream clock source and behaves as a source to its downstream devices.
Ordinary Clock (Member clock, Slave) is the device which has only one port and with this port it synchronizes itself with the upstream source.
Transparent Clock is the device that has multiple ports connected to boundary clock and ordinary clocks as a bridge between them. It does not behave either clock source or client. Transparent clock updates the correction field within PTP event messages to compensate for the transmit delay.
Generally, the first three clock types are used. Sometimes there can be an additional Transparent clock in the networks.
You can DOWNLOAD Cisco Packet Tracer and GNS3 Labs.
As we have mentioned before, there are PTP enabled and non PTP devices in a network. If you would like to enable PTP on a Cisco device, you should enable it globally on that router. To do this, we will use “ptp” command.
ptp {mode {boundary | e2etransparent | forward} | priority1 value | priority2 value}
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ptp
Router(config-ptp)# commit
Router(config-ptp)# end
To check the clock provided by PTP, we use, “show ptp advertised-clock” command.
Router# show ptp advertised-clock
Clock ID: Local Clock (17aa45fffe22f865)
Clock properties:
Priority1: 128, Priority2: 128, Class: 248, Accuracy: 0xfe
Offset scaled log variance: 0xffff
Domain: 0, Time Source: Internal, Timescale: ARB
Current UTC offset: 24 seconds
Here, there is a Clock ID which is derived from router’s MAC address by default. Beside the other properties of this clock is showed with “show ptp advertised-clock” command.
To configure PTP Master, we use “ptp” command under interface. When we enable ptp under an interface, by default, it becomes PTP Master.
ptp {announce {interval value | timeout value} | delay-req interval value | enable | sync {interval value| limit value}}
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interfaceGigabitEthernet 0/0/0
Router(config-if)# ptp
Router(config-ptp-if)# commit
Router(config-ptp)# end
To check PTP Master state of an interface, we will use “show ptp interface interface” command for this interface.
Router# show ptp interfaces gigabitEthernet 0/0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 is in Master state
PTP port number: 2049
IPv4 transport: IPv4 address 10.0.0.1
Linestate: Up
Mechanism: Two-step delay-request-response
Sync rate: every second
Announce rate: every 2 seconds, timeout 3 intervals
Min Delay-Request rate: every second
CoS: 6, DSCP : 46
Platform capabilities:
Supported: One-step, Ethernet, Multicast, Slave
Not-supported: IPv6
Max-Sync-rate: 3 per second
0 Unicast peers
To configure PTP Slave, we specify master with “master { ipv4 | ethernet }” command after “ptp” command.
Router #configure terminal
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
Router(config-if)# ptp
Router(config-if-ptp)# master { ipv4 | ethernet }
Router(config-if-ptp-master)# commit
There can be more than one slave interfaces. In such a situation, PTP will select the best Master and that interface will be the Slave. We can set foreign Master priorities under slave interfaces also.
To verify PTP configuration, we can use “show ptp interfaces” command. With this command, we can see details of PTP configuration and Master table.
Router# show ptp interfaces
Thu Mar 29 18:03:15.254 PDT
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is in Passive state
PTP port number: 2049
IPv4 transport: IPv4 address 10.0.0.1
Linestate: Up
Mechanism: Two-step delay-request-response
Sync rate: every second
Announce rate: every 2 seconds, timeout 3 intervals
Min Delay-Request rate: every second
CoS: 6, DSCP : 46
Platform capabilities:
Supported: One-step, Ethernet, Multicast, Slave
Not-supported: IPv6
Max-Sync-rate: 3 per second
Master table:
MAC-address 1346.AA56.BA67: priority 5
IPv4-address 10.0.0.1: priority not set
IPv4-address 13.AA.BA.56: priority not set, multicast
0 Unicast peers
PTP and NTP are two clock synchronization protocols. They have some similar and different characteristics. Here, we will focus on the differences of PTP and NTP. Below, you will also find a PTP and NTP Comparison table.
NTP is the abbreviation of Network Time Protocol and PTP is the abbreviation of Precision Time Protocol.
NTP provides millisecond accuracy while PTP provides sub-microsecond accuracy. This accuracy level makes PTP better clock protocol. With additional hardware, NTP can provide millisecond level accuracy. But this time, PTP provides nanosecond level.
NTP is used in WAN networks and public networks. PTP is used in different networks according to its version. PTP version 1 is used for LAN and PTP version 2 is used for WAN.
NTP provides security by using hash codes. PTP provides this security with cryptography.
These two protocols are also used in different fields. NTP is used in home automation, industrial automation, telecommunication, networking etc. Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is used more critical applications like financial transactions, aircraft monitoring.
Leave a Reply