- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
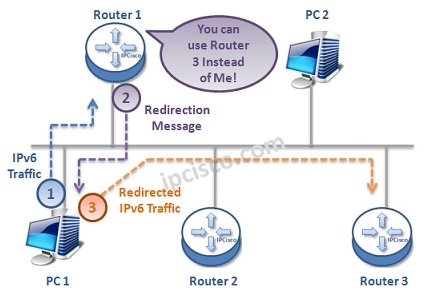
Table of Contents
IPv6 NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) is the Protocol that provide Network Nodes’ Discovery as its name implies. In the IPv4 World, we were using ARP, but in IPv6 world there is no ARP. Instead, ICMPv6 based NDP is used for Neighbor Discovery. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses are used to discover neighbors. With NDP Mechanims, nodes in the same link advertise their existance, learn about neighbours, track neighbor reachability etc.
NDP, uses five types of ICMPv6 Messages and a specific Multicast Address type, Solicited-node Multicast Address for its operations.
So, what are these five ICMP Messages used by NDP mechanims? These ICMP Messages are given bellow:
Neighbor Solicitation Message is used to request the link layer address of a neighbour. It is also used to check neighbor availability with the same link layer address. Another usage of this message is on dublicate address detection.
Neighbor Advertisement Message is used as a response to Neighbor Solicitation Message and if there is a change of link-layer address.
Router Solicitation Message is the message that requests Router Advertisement immediately without waiting the next interval. When an interface is enabled, this message can be sent.
Router Advertisement Message is the message that advertises the presence of the router with various parameters. This can be a periodic message or a response to a Router Solicitation Message.
Redirect is the message used to inform the hosts about a better first hop to a destination.
By the way, all of these messages should use Link-Local addresses (FE80::/64).
IPv6 NDP has some important roles. Let’s check these roles:
Let’s explain these roles one by one and see NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) Operations.
In IPv6, Prefix and Parameter Information is discovered with ICMPv6 Messages. These information is carried by Router Advertisement Messages. With this information, Hosts become familier that which IPv6 Prefixes are in that Link and what are the parameters.
In IPv6 NDP Concept, the next-hop is determined like IPv4, towards the longest match. If there is no match, then to the Default Route.
IPv6 NDP Concept also provides Neighbor unreachability detection. This is also done with ICMPv6.
In IPv4, we can manually configure or rely on DHCP to give a Gateway Address to an Host. But this is a little different in IPv6. In IPv6, with Router Discovery Mechanism, Routers on the link can be detected by the Hosts. This is done with two ICMPv6 messages that are given below:
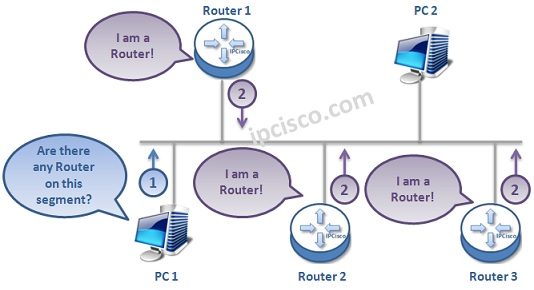
“Are there any Router on this Link?”
Routers on the link send Multicast Router Advertisement Messages as a response. With this message, they say that,
“I am a Router in this link”.
Multicast Router Solicitation Message can be sent to receive immediate Router Advertisements without waiting the periodic Router Advertisement Message interval. With this message, host learns the required IPv6 information quickly. The destination of this message is all routers multicast address, FF02 :: 2
Router Advertisement Messages are sent by the routers both periodically to advertise themselves or as a response to a Router Solicited Message. The ICMPv6 message type of this message is type 134.
According to the reason of this message, the destination address of the message changes. If the message is sent periodically to advertise the router, the destination will be all nodes multicast address, FF02::1. If it is sent as a response to a Router Solicited Message, then the destination will be the source of the Router Solicited Message.
Especially for Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC), Router Advertisement Messages are important. The M bit in Router Advertisement Messages detemines the type of address autoconfiguration. If M bit is set to 1, stateful auto address configuration is used. If M bit is set to 0, then stateless autoconfiguration, SLAAC is used.
In IPv4, ARP is used for Address Resolution. But in IPv6 there is no ARP. Instead, IPv6 uses ICMPv6 for address Resolution. Two messages of ICMPv6 is used for this job. These ICMPv6 messages are given below:
A Host on the link sends a Multicast Neighbor Solicitation Message and try to discover Link Layer Address of a neighbor on the same local link. The destination of this message is the Solicited-node multicast address of the corresponding address. The meaning of this Neighbor Solicitation Message is :
“What is Marry’s Link Address?”
The source address of this Neighbor Solicitation Message is the IPv6 address of the sender device and the destination address is the solicited-node multicast address that corresponds to the IPv6 address of the destination. The data portion of the message includes Link Layer address of the sender. After the neighbour receives this message, it sends a reply with Neighbor Advertisement Message that tells,
“I am Marry and this is my Link-Local Address”.
The source address of this Neighbor Advertisement Message is IPv6 address of the neighbor and the destination address is the IPv6 address of NS source. The data portion of the message includes Link Layer address that is requested.
Neighbor solicitation messages are also used to check the reachability of the neighbor. When they are used for this purpose, the destination address of the message is the neighbor IPv6 address.
Neighbor Advertisement Messages can be sent both as a respose to the Neighbor Solicitation Message or as an immediate propagate of new information like link-layer address change. The second type message is used to inform the network after a change. At this time, the destination of the message is All-nodes multicast address (FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:1).
In IPv4 world, ICMPv4 Redirection messages are being used. With IPv6, this is also changed and ICMPv6 Redirection Messages (Type 137) are being used. With this message, router informs the node about a better path to a destination. In other words, router offer another way to the host.
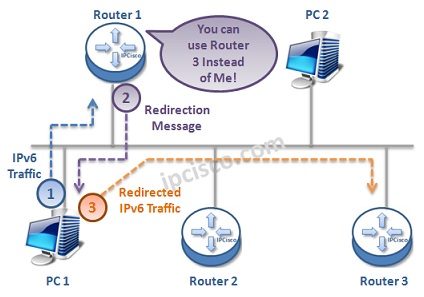
“Instead of Me, you can use Router3”.
The aim of these messages isto help the host to make the most efficient local routing decision.
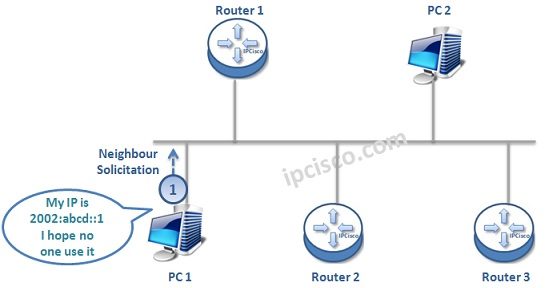
In IPv4 there is a mechanims called “Gratuitous ARP”. This is the ARP type that is used for avoiding duplicate IP addresses. IPv6 has a similar mechanism. In IPv6, this is done with special type Neighbor Solicitation Message. Host sends an unspecified IPv6 address to the destination of the solicited-node multicast address of this IPv6 before using it. And it waits any reply from the network. If a reply Neighbor Advertisement Message comes as a reply, then it does not use this IPv6 address.
Leave a Reply