- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
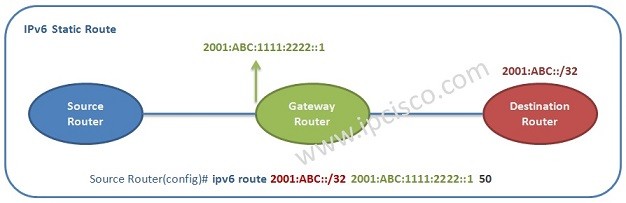
Table of Contents
As you know, Static Route is the route that you manually define on a router.This is done when we do not want to use Routing Protocols for small part of a network. Or, in large networks some small amout of routing is done via static routing. For IPv6, we use IPv6 Static Routes.
To define a IPv6 Static Route, we will firstly write the prefix OR the network we will reach and then, the next hop to reach that network.
If you would like to test your NRS I Knowledge, you can do this on Nokia NRS I Question Page.
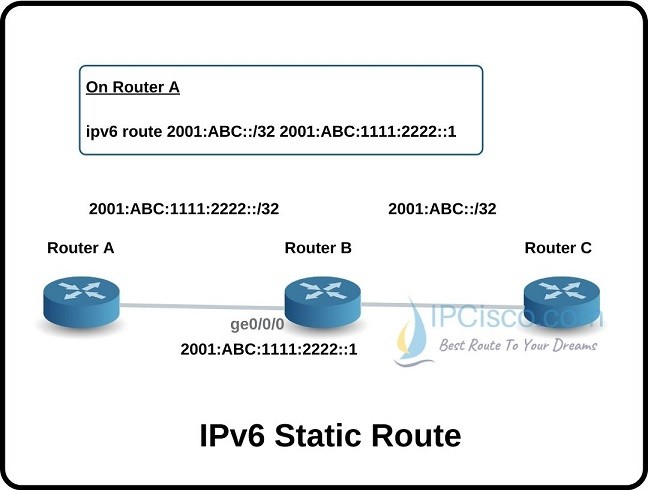
As IPv4 static routes, we can also use static routes for IPv6 addresses. Here, the only difference is using IPv6 addresses. In other words, the destintion and the next hop addresses are IPv6 addresses in IPv6 static routing configuration.
For example, let’s do an IPv6 static route configuration example with 2001:ABC::/32 network and 2001:ABC:1111:2222::1 next hop adres. To do this configuration, we can use the below command:
Router(config)# ipv6 route 2001:ABC::/32 2001:ABC:1111:2222::1
The Default Route is a type of static routing. They are used whenever the destination of the packet is not reside in the routing table of the router. So, the traffic is sent to the destination mentined in default route if there is no route information in the router about this destination.
Default rotues for IPv4 is configured with IPv4 addresses. IPv6 Default routes are configured with IPv6 addresses. For this, in IPv4, we use 0.0.0.0/ source default route and in IPv6, we use ::/0.
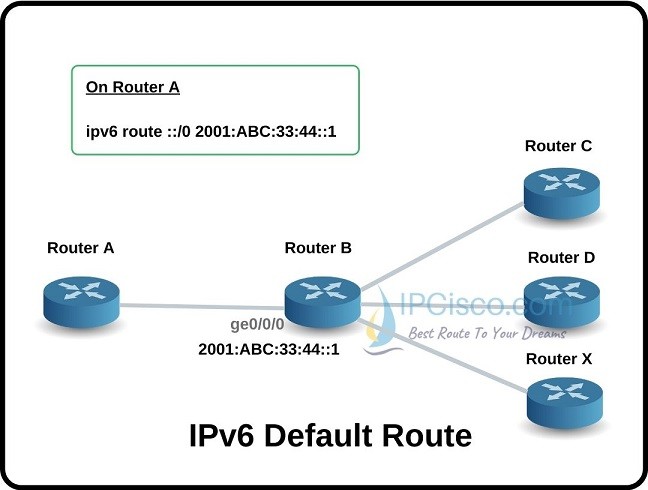
For IPv6 default route configuration, after “ipv6 route” command, we will use IPv6 default source IP address (::/0). And then, we will use next hop IPv6 address.
Below, you can find a default IPv6 route example with the next hop 2001:ABC:33:44::1.
Router(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:ABC:33:44::1
With this IPv6 Default Route Configuration, if the destination address of the packet is not known, the traffic is sent to the 2001:ABC:33:44::1 interface by default.

Leave a Reply