- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
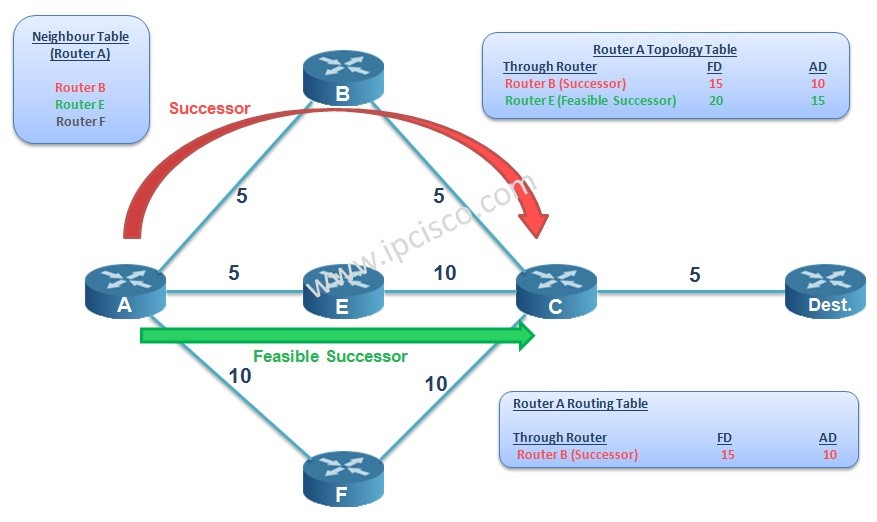
Table of Contents
EIGRP is an Enhanced Dynamic Routing Protocol that provide many methods for a good Routing Protocol implementation. In this lesson, we will focus on some of the key methods of EIGRP and we will learn these key methods with many EIGRP config examples. We will practice on some of the Key EIGRP Configuration scenarios that will help you to do a better EIGRP implementation.
Here, we will learn the below methods of EIGRP:
Now, let’s focus on these key EIGRP methods, learn and configure each of them with different EIGRP Configuration Examples.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP ENCOR Practice Tests and CCNP ENARSI Practice Page Page!
By default EIGRP summarizes the classfull addresses. So generally “no auto-summary” command is used on Cisco router to avoid this situation. In the EIGRP Configuration below, you can find an example of EIGRP Route Summarization.
Router (config) # router eigrp 100
You can also use EIGRP Summary Routes manually. You can use this by “ip summary-address” command on Cisco Routers. Below there is a route summarization with 10.0.0.0/8 prefix.
Router (config) # interface fa0/1
If you want to prevent one interface or all interfaces to receive EIGRP update and EIGRP hello packets , you can use “passive interface” command. By using this command, no update and hello packets come to that interface anymore.
For example, with “passive interface” command, you can prevent fa0/1 to receive update and hello packets like below EIGRP Config.
You can also prevent all the interfaces to receive these packets and then you can open the ones you want. Below, firstly we prevent all interfaces and then allow fa0/5 and fa0/6.
Router (config) # router eigrp 100
In EIGRP, Multicast Address 224.0.0.10 is used . If you want , you can change this to a specific neighbour address with “neighbour ip-address” command on Cisco routers. You can use this command like below:
Router (config) # router eigrp 100
EIGRP Stub router is the router that is not a transit router and only has one EIGRP neighborship. EIGRP Stub provides less queries. You can configure EIGRP Stub, like below:
Router (config) # router eigrp 100
Router (config-router) # eigrp stub [receive-only, connected , static, summary, redistributed]
After stub command, you can optionally use some parameters. These parameters are receive-only, connected , static, summary, redistributed. The meaining of these parameters are given below:
Receive-only : Update are not shared with neighbors.
Connected : Only connected routes will be advertised.
Static : Only static routes will be advertised.
Summary : Only summary routes will be advertised.
EIGRP supports MD5 Authentication.For reliable transfer between two EIGRP Neighbor, MD5 Authentication is used. The authentication parameters between two neighbours must match. Below, you can find an example configuraiton for EIGRP Authentication Configuration on Cisco routers.
You can test your Routing Knowledge on CCNP ENCOR Practice Tests and CCNP ENARSI Practice Page Page!
Leave a Reply