- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
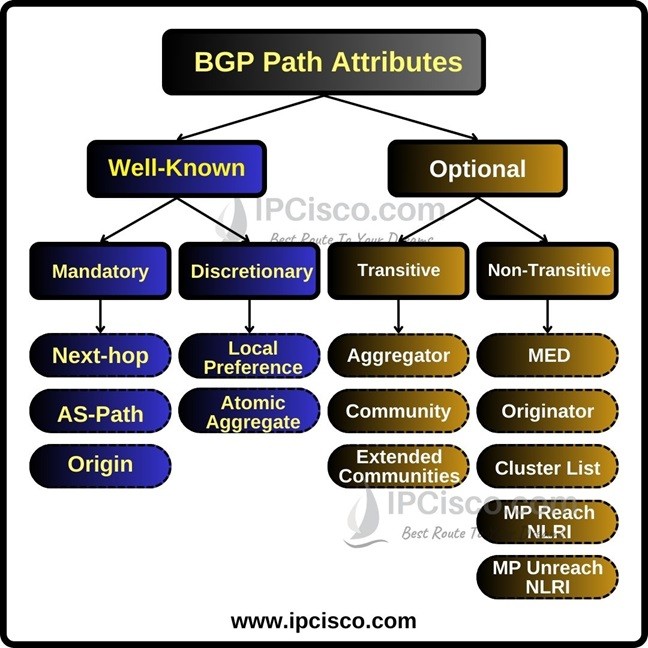
Table of Contents
BGP uses BGP Path Attributes to determine the Best Path to a destination. According to BGP Best Path Algorithm, BGP Path Attributes are used to determine the BGP Best Path selection.
With these Path Attributes, network administrators can manage the BGP Traffic and determine way of the BGP traffic flow.
You can also test yourself on BGP Quizes Sectionfor your BGP Path Attribute knowledge.
BGP Path Attributes divide into two groups. These classes are Well-Known and Optional path attributes. These two groups divide also into two subgroups again. These four BGP Path Attribute sub groups are:
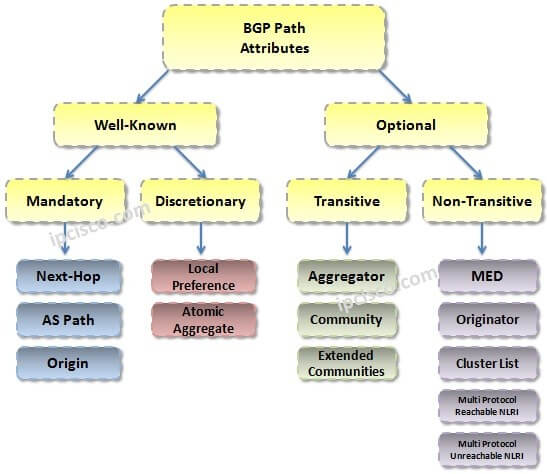
Optional Transtive : Aggregator, Community
Optional Non-transtive :Multi-Exit-Discriminator (MED) , Originator ID, Cluster List
There is also one extra important BGP Path Attribute. This attribute is, Cisco Proprietary, BGP Weight Attribute.BGP Weight Attribute is only used on Cisco router and it is the first step of BGP Path Selection algorithm for Cisco devices.
You can also test yourself on BGP Quizes Sectionfor your BGP Path Attribute knowledge.
The names and categories of these BGP Path Attributes were really confusing for me too:) To make this information more permanent for you, lets make an analogy.
We will discuss these BGP Path Attributes detailed and with Configuration examples in the following posts as our previous lesson, BGP Configuration on Packet Tracer.
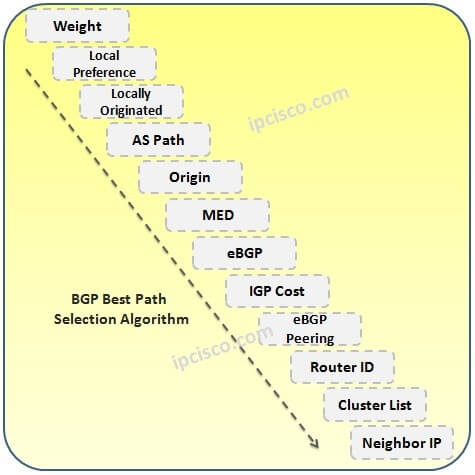
As you know routing protocols have Administrative Distance (AD) values for preferability. And different vendors have different Administrative Distance (AD) values for the same routing protocols. This is also valid for BGP.
By the way “Administrative Distance (AD)” term is used in Cisco terminology. For Juniper, Nokia and Huawei, instead of Administrative Distance (AD), “Preference” is used.
Some main vendors and BGP AD(Preference) Values are below:
In Cisco routers two AD values used for BGP. For the routes learned outside the AS (eBGP routes) this value is 20, while the AD for iBGP and locally-originated routes is 200.
In Juniper and Alcatel-Lucent routers the Administrative Distance phrase changes to Preference value.
In Juniper routers Junos OS uses the same preference value for both EBGP and IBGP. This value is 170. However, difference between vendors has no operational impact because Junos OS always prefers EBGP routes over IBGP routes.
Preference value is also 170 in Alcatel-Lucent routers.
Lastly, for Huawei, Preference values are 255 for both EBGP and IBGP.
Very Easy and Nice Explanation
Thank you very much Salman;) Enjoy!