- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
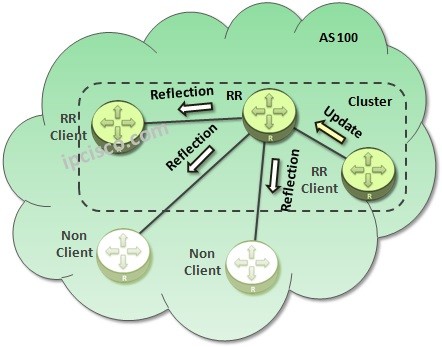
Table of Contents
By default iBGP Peers need to be Full mesh together. BGP Route Reflector (RR) is a BGP Mechanism used to bypass this iBGP Full Mesh requirement and provide all iBGP Routing information to all iBGP peers. With this mechanism less bandwith and CPU usage is provided in BGP Topology. This is important especially for large networks.
BGP Route Reflector (RR) system is a Client/Server System. All the BGP Route Reflectors are Server and the other iBGP peers are Client in this topology. BGP Route Reflectors are connected to all iBGP Peers and they learn the BGP routes form iBGP Peers, then they send this routes to orther iBGP Peers. Here, full mesh requirement is bypassed, all iBGP peers do not need to be connected eachother. So, the iBGP connections in a BGP topology is reduced.
You can test you BGP Knowledge on BGP Questions Page.
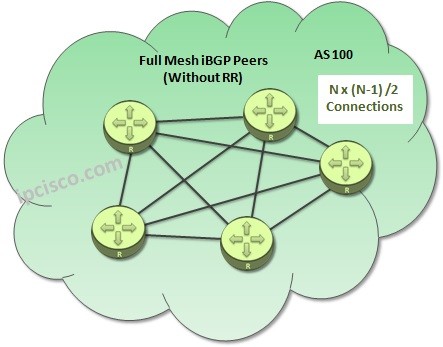
Think about the below BGP Topology. In this BGP Topology, without Route Reflector mechanism, all the iBGP Neigbors need to be connected together as full mesh.
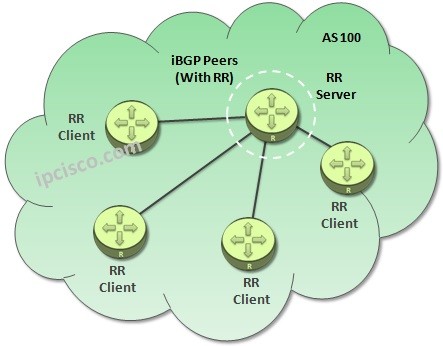
By using a Route Reflector, this Full mesh requirement is bypassed. One router is selected as RR and the other routers are connected and send updates to RR Router only.
There are three different Router roles in Route Reflector mechanism of BGP. These router roles are given below:
With Route Reflector mechanism, the Router that will be a Route Reflector (RR) become RR Server and the other iBGP neighbors are configured as RR Clients on this RR Server. These RR Clients send updates to RR Server and the full mesh requirement is bypassed. Without fullmesh, all iBGP Routers learn all BGP Routes. This mechanism is also a Hub and Spoke toplogy. Route Reflectors are Hubs and RR Clients are Spokes here.
RR Server and RR Clients are together form a “Cluster”. Non clients are the routers that is not located in this Cluster.
In simple BGP designs there can be one Route Reflector. But there can be one more RRs in a BGP Topology. Especially for redundancy purpose, two Route Reflectors are used in large networks. Using one more RR prevent one node failure effects and provide a redundant BGP topology.
Different RRs can belong to the same Cluster or to different Clusters. In a BGP Topology, different clusters must be connected together over at least one RR. But generally all the RRs in different clusters are connected together as full-mesh. The other Non Client peers are also included to this full mesh topology. The RR Clients of each cluster are connected to their RR or RRs one by one.
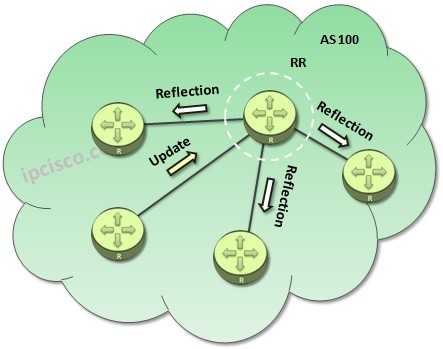
Route Reflection is done between RR Server an RR Clients in the cluster. There are different cases for this process. Let’s check these cases:
Leave a Reply