- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) is one of the MPLS Label Distribution protocols that is used for label signaling in MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching). So, how LDP works and how is the label distribution done? In this lesson, we will explain these processes detailly with an example.
LDP uses IGP (OSPF, EIGRP etc.) to determine the best path to a destination. So, before LDP configuration, IGP or in other words Routing Protocol must be configured and converged in the network.
After Routing Protocol Configuration, LDP is enabled on the routers and LDP Adjacencies are established.
The adjacent routers check their routing tables and sends labels to the upstream router about the networks that they know. Here, there is a key information. Label Distribution is done in the opposite direction of the label swapping. In other words, label learning is done in one direction and label swapping is done in another direction.
When the Upstream Router learns the labels, it stores them in the Label Databases with the associated networks. And whenever a packet comes with the destination of that network, it assigns this label and send the packet to the Downstream Router.
With such a mechanism, all the routers learn all the possible destinations and associated labels.
Now let’s do an example for this MPLS Label Distribution.
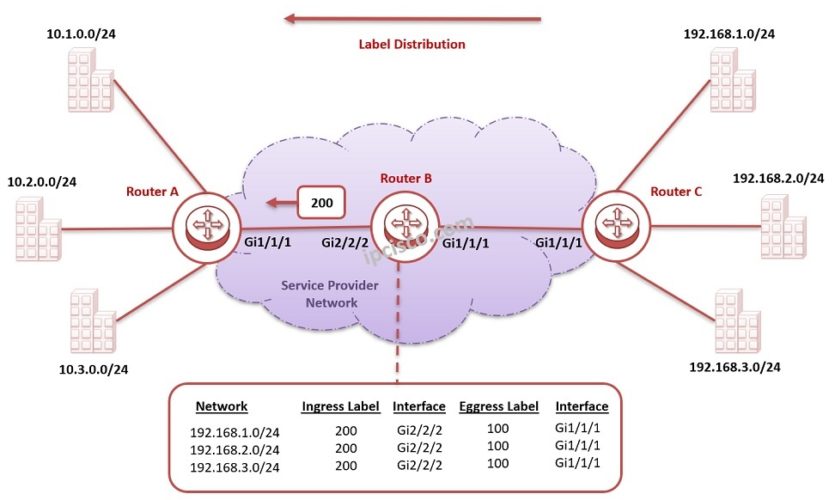
As you can see in the below topology, we have three routers and six different networks connected to these routers. Router A and Router C are Provider Edge routers and Router B is a Provider router.
After the LDP adjacencies are established, Router C checks its routing table and assigns a label for the networks, 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24 and 192.168.3.0/24. The assigned label by Router C is 100 for these networks and send it to Upstream Router, Router B.
After that the Upstream Router, Router B receives this label and records it in its Label Databases as Egress Label.
Then, it sends the same networks with a different label value, with label 200 to its Upstream Router, Router A.
Router A receives the label and records it in its Label Database as Eggress Label.
The Label tables are filled with this method for all the routers in the service provider network. The MPLS Label Distribution or in other words Label Learning is also done for the reverse direction, from Router A to Router C.
After all the labels are learned, now let’s see how the packets are send from Router A to a network behind Router C. Here, our destination will be 192.168.2.0/24.
Leave a Reply