- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
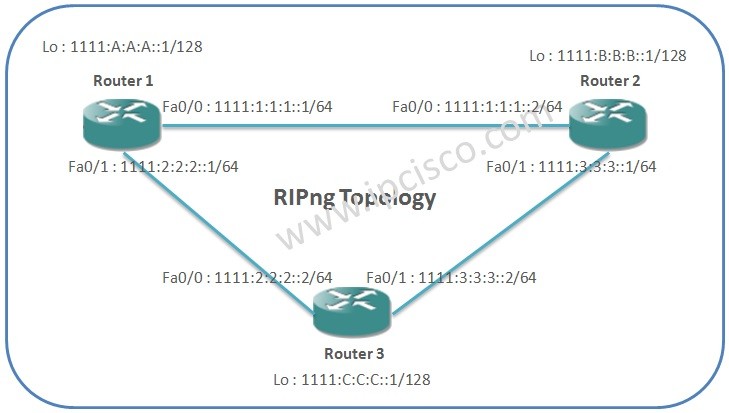
Table of Contents
RIPng (RIP Next Generation)is the IPv6 available next level protocol of RIPv2. In modern large networks, generally RIP is not used and also RIPng. But as a basic protocol, it is still used in many small networks.
Basically, the characteristics of these two version is same. As we discussed before in the RIP article, RIPng has the below similar characteristic as RIPv2:
• Distance vector protocol
• Uses “Hop count” as metric
• The default administrative Distance is 120
• Uses Split Horizonin, Poison Reverse
• Uses periodic (30 seconds) and triggered updatas
As you can see above, RIPng is almost the same as RIPv2. But there are some additional differences because of the supported IP version (IPv6). Let’s chek this differences one by one:
RIPv2 is the protocol that is used with IPv4. With this new version of RIP, RIPng, IPv6 addresses are supported. The neighbourship is established with the IPv6 addresses.
Here, with the support of the IPv6 addresses, some of the commands are added to the Cisco IOS. So, similar but different commands are used for RIPng.
RIPng is established over interfaces. If an interface needed to be in the RIPng network, RIPng network is added under this interface. In RIPv2, we use network command to add subnets (networks) to the RIP network. But with RIPng, like other IPv6 routing protocols, interfaces individually used as member of RIPng network and RIPng membership command is added under interface configuration.
RIPv2 uses UDP port 520. This port changes a little with RIPng. RIPng uses UDP port 521.
