- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is one of the multicast protocols used for user registration to multiple multicast groups. There are different versions of IGMP. These are IGMPv1, IGMPv2 and IGMPv3. The most used IGMP version is IGMPv2 today. But the enhanced one is version 3. In this lesson we will focus on what is IGMP v3 and what is new with this enhanced Internet Group Management Protocol version. You can also check multicast routing protocol PIM with this lesson.
Table of Contents
IGMP v3 is the latest version of Internet Group Management Protocol. It is enhancement over version 2. There are some similarities with other IGMP versions and there are some differences.
IGMPv3 was firstly defined with RFC 3376. Then it is updated with RFC 4604.
IGMP v3 mechanism uses a little similar and a little different method than other versions. So how does IGMPv3 work? Let’s explain the steps one by one.
First of all, let’s explain a Multicast Group Join. Multicast receivers send IGMPv3 Membership Report to the address 224.0.0.22. This is the address of all version 3 capable routers. This report is sent with an empty EXCLUDE list.
For Specific Multicast Channel Join, this time receivers send IGMPv3 Membership Report to 224.0.0.22 twice. But this time source unicast addresses are included to INCLUDE list.
IGMPv3 General Membership Queries are sent to 224.0.0.1, periodically by the local multicast router. All IGMP v3 receivers replies with IGMPv3 Membership Report.
To leave a group, a source or a channel, there is no specific message in version 3. As you remember, IGMv2 is using a specific leave message for this job. But there is no version 3 specific leave message. IGMP v3 uses Membership Report with an empty INCLUDE list is used instead of specific leave message.
Source Specific Multicast
If we compare IGMPv2 vs IGMPv3, the main difference is this! IGMPv3 is used with PIM Source Specific Multicast. Source Specific Multicast is a PIM method with which multicast receivers can determined the multicast source. In other words, a multicast receiver can receive multicast service from a desired multicast source. In this mechanism, Internet Group Management Protocol v3 is responsible for the relationship of users and source.
IGMP Source Filtering is the mechanism used specifically with IGMP v3. With this mechanism, multicast client can filter the source group and source address that it wants to receive multicast traffic.
There are two modes of IGMPv3 Source Filtering. These are:
In Include Mode, multicast receivers use listed unicast source addresses for the multicast groups.
In Exclude Mode, multicast receivers use not listed unicast source addresses for the multicast groups.
IGMPv3 itself uses two different message types. These two messages and their type number values are given below:
For interoperation with the other versions, IGMP v3 must support the below message types:
There are three variants of IGMPv3 Query message. These are:
General Queries are sent to all system multicast address, to 224.0.0.1.
Group-Specific and Source-Specific Queries are sent to the related multicast address.
IGMP v3 Membership Reports are sent to 224.0.0.22. This is the address of IGMv3 capable listeners.
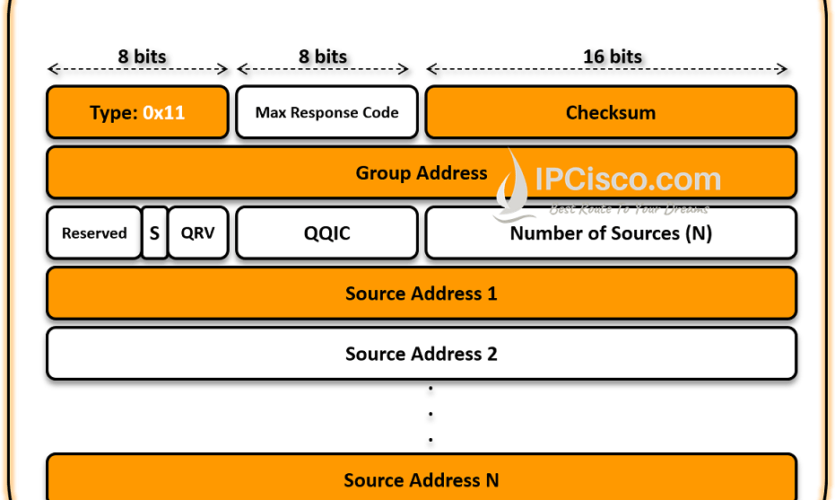
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 messages has less areas than IGMP v3 messages. There are two common messages types used with version 3 as we have mentioned above. The areas of these message fields are given below.
In IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 there are one group record in membership report message. But in IGMP v3, there are multiple group records in membership report message. Each of the group record has the below areas:
IGMP versions are backwards Compatible. So, a router which supports IGMPv3, can supports also IGMPv1 and IGMPv2. If your router can be configured with IGMP v3, it can be configured with other versions.
Leave a Reply