- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
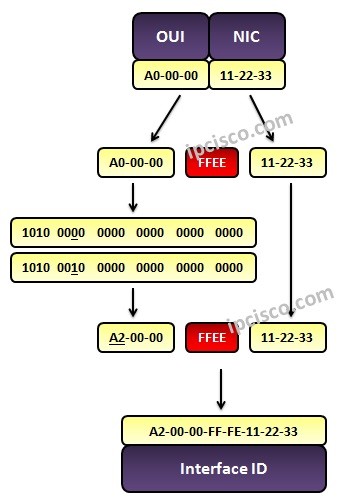
Table of Contents
IPv6 has different address types. One of the important and widely used IPv6 Address type is IPv6 Link Local Address. Every IPv6 enable interfaces must have a Link-Local Address either with manual configuration or auto-address configuration. IPv6 Link Local Address is the address used between Point-to-Point interfaces and provide IPv6 Neigbor Discovery.
Point-to-point interfaces do not need a Global IPv6 Addres to communicate each other. Instead, they use IPv6 Link Local Addresses for point-to-point communication. And Router do not forward these Link-Local Addresses because they are used only on a single link.
There are different prefixes are used with different IPv6 Address Types. The Prefix of IPv6 Link Local Addresses is FE80::/10. All the other Prefixes used with IPv6 Address Types are given below:
IPv6 Link Local Addresses can be configured in two ways. These Link-Local address configuration ways are :
Auto-Address Configuration is done automaticaly with the help of Link Local Prefix (FE80::/10) and Interface Identifier in EUI-64 Format. This is the widely used method to configure a IPv6 Link Local Address.
The second way is Manual Configuration. In this configuration way, we use a manual router command to configure IPv6 Link Local Address. This command is “ip address link-local” in Cisco Routers.
IPv6 Link Local Auto-Address Configuration is the widely used Link-local address configuration method. With this method, IPv6 Interface ID with EUI-Format is used.
So, what is EUI-64 Format? Let’s explain.
As you know IPv6 Addresses are 128 bits long. The first 64 bits of these addresses are used as Network Id and the remaining 64 bits are used as Interface ID. This interface ID is produced with the help of the interfaces hardware address (MAC addres) with EUI-64 Format. Now, let’s explain the EUI-64 Format Interface Identifier configuration step by step.
You can also test your IPv6 Knowledge on IPv6 Questions Page.
IPv6 link-local addresses are defined by RFC 4291, IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture. In this RFC, all the IPv6 Address types are covered.
There are different IPv6 address types and each has a prefix. The prefix for IPv6 address is FE80::/10. This is the theorical value. In practice, only FE80::/64 is used.
Like IPv6, there are also link-local addresses in IPv4 but we know them as APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing). This is defined in RFC 3927, (Dynamic Configuration of IPv4 Link-Local Addresses). The range of IPv4 link-local addresses, APIPA addresses is 169.254.0.0/16. (169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255).
By the way, there is a difference between IPv4 and IPv6 version of these addresses. In IPv4, link-local addresses, apipa addreses are used when DHCP fails to give an ip address to the interface. In other words, if you see any ip address in the range (169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255), this means that there is no ip address on the interface.
Leave a Reply