- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this lesson, we will learn other Spanning Tree Protocol Convergence Mechanisms; Loop Guard, Uplink Fast, Backbone Fast and UDLD. Now, let’s learn each of these switch mechanisms and their roles one by one. To learn about other STP Convergence Mechanism, you can visit BPDU Filter | BPDU Guard | Root Guard | Portfast lesson.
Table of Contents
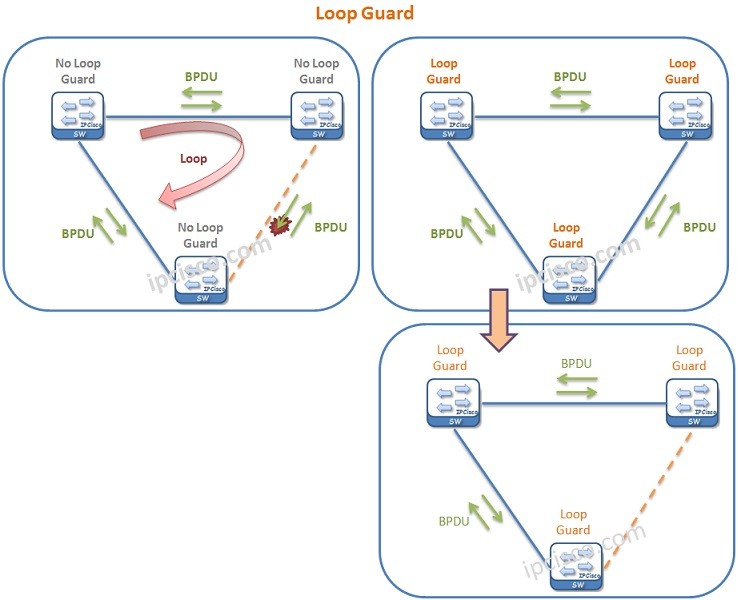
STP Loop Guard is the STP mechanims that is used to protect the network against the layer 2 loops. In other words it is a loop protection mechanism.
For example a switch can send BPDU but can not receive any BPDU from the other switch. And this is detected by UDLD. If the Loop Guard is configured, Loop Guard puts the port in “Loop Inconsistence State” instead of going through Forwarding state in this situation. But if there is no Loop Guard, then, the port continue to sends Bridge Protocol Data Unit and goes through Forwarding State. In such a situation, a Layer 2 Loop occurs. Loop Guard is mainly used to avoid such cases.
To configure Loop Guard globally on a Cisco switch, you can use “spanning-tree loopguard default” command.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree loopguard default
Beside, to enable Loop Guard on a specific interface, you can use “spanning-tree guard loop” command.
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard loop
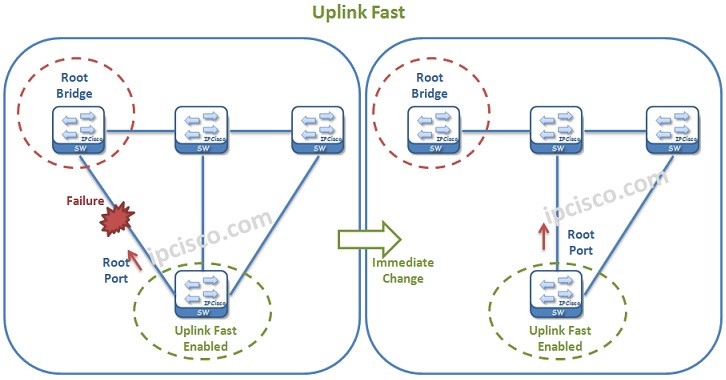
Uplink Fast is the convergence accelerator mechanims that can be configured on only Access switches and on the uplink ports. With Uplink Fast mechanims, if a port fails, then the second way on the uplink become active imediately. This immediate access, reduces the convergence time.

Uplink Fast can be enabled globally with the “spanning-tree uplinkfast” command on a Cisco switch.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree uplinkfast
Backbone Fast is the mechanims, that is used to detect indirect link failures in the backbone. Think about a topology that is consist of different connections. Normally, a problem occurs on the link that connects two neighbor can be detected by them. With Backbone Fast, an indirect failure can also be detected. Here, indirect link means that any link that is different from the link between neighbors.
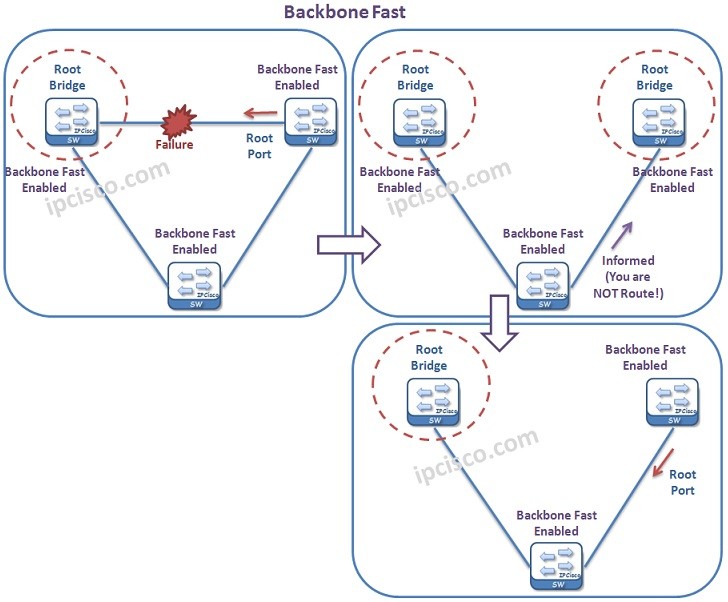
To configure Backbone Fast, we need to configure it on all the swithes in the network. To do this, we will use “spanning-tree backbonefast” command globally, on all the switches in the network.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree backbonefast
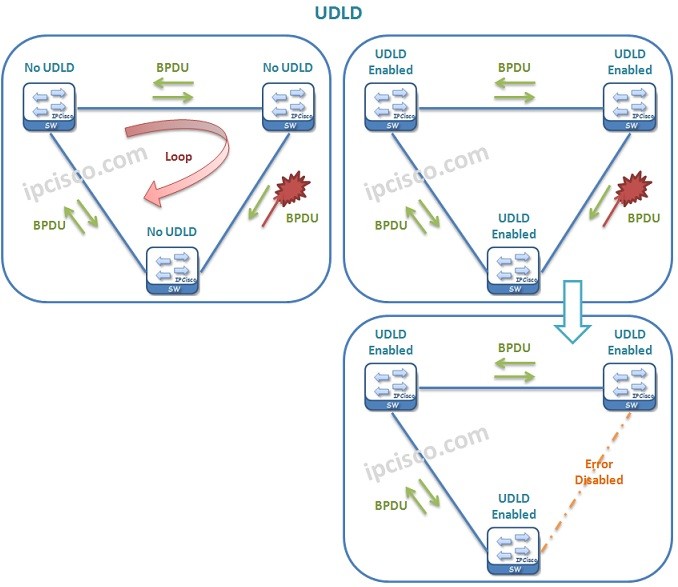
UDLD (Unidirectional Link Detection) is the mechanims that detects one way traffic between neighbors. For a stable link, the transmission must be bidirectional between the neighbors.
If UDLD detect a failure in aggressive mode, it puts both end in the Error Disabled mode. If normal mode is used, then it puts only UDLD detected port in Error Disabled mode. Other end only see that the port is down.
To configure UDLD, the required commands are below for Cisco switches:
For global Unidirectional Link Detection configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# udld enable
Or
Switch(config)# udld aggressive
For a specific port configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)# udld port enable
Or
Switch(config-if)# udld port aggressive
To disable, you can use “no udld port” command under the port.
To check the status of UDLD, you can use “show udld” command.
Switch# show udld
To verify STP Mechanims, you can use “show spanning-tree interface interface-name detail” command. In the details of any interface, all the STP related mechanims situations are showed.
Switch# show spanning-tree interface interface-name detail
Leave a Reply