- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
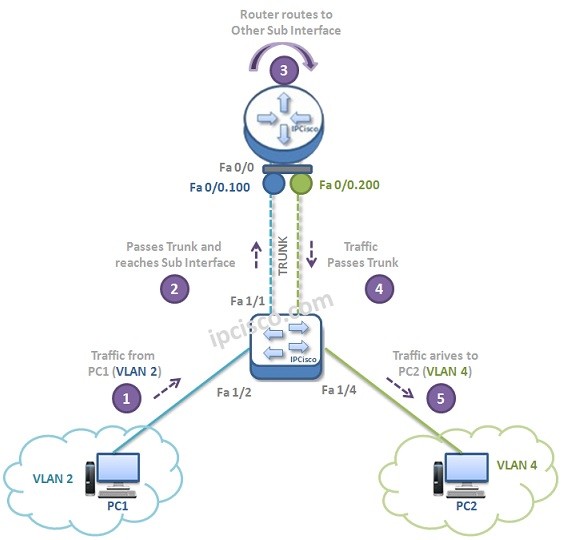
Table of Contents
VLANs are used to separate different subnetworks in a big network. If you divide a network with VLANs, each of these new VLANs become a different network. Devices reside in different networks, can not communicate with the other devices reside in different networks withour routing. This is also true for VLANs. Different VLANs can not communicate without routing. The routing between VLANs is used to provide this communication. This is called “Inter VLAN Routing”.
Inter VLAN Routing is the Routing that is done between different VLANs. There are two ways to do Inter VLAN Routing:
Let’s see each of this methods, detailly.
Router on Stick Topology, in other words, External Router Topology is the first way for Inter VLAN Routing. For Router on Stick Topology, a Layer 3 device, a router or a multi layer switch is required. Basically, this Layer 3 device reside on the top and with one of its interface it is connected to the switch that has VLANs on it. This physical interface of the router is divided into sub interface. This sub interfaces are created for each VLAN. Here, each router Sub Interface will be the gateway of the related VLAN.
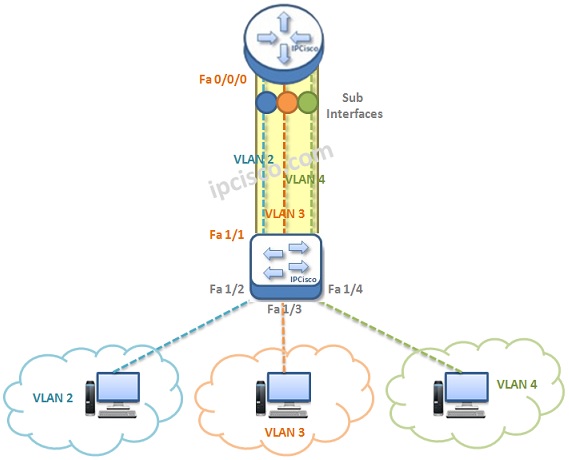
Without Trunk link, this is achieved with seperate links for each VLAN. But this is not a feasible solution.
Inter VLAN Routing with Router on Stick topology can be done for the VLANs on Layer 2 or Layer 3 switches. But here, there is a single Layer 3 device, a router or a multilayer switch is required at the top. For its configuration steps, it is an easy way but for security perspective, single router at the top means also, single point of failure.
Think about the below topology. In this topology PC 1 in VLAN 2 needs to communicate with PC2 in VLAN 4.

1. Traffic came to the switch form PC 1 (VLAN 2). 2. Traffic crosses the trunk and reaches to the Sub interface Fa 0/0.100 associated with VLAN 2. 3. Router routes the traffic to the other Sub Interface Fa 0/0.200 associated with VLAN 4. 4. Traffic crosses the trunk. 5. Traffic arrives to the PC2 (VLAN 4).
Now, let’s talk about the configuration steps of Router on Stick Topology.
In the first step, required VLANs are created on the switch and required host ports are assigned to this VLANs.
In the second step, Trunk port is configured and the allowed VLANs are mentioned.
At the third step, the configuration on the router is done. On th physical interface of the router that connects to the switch, sub interfaces are created. For each sub interface, encapsulation method (dot1q) and the specific ip address is configured.
Lastly, verification of Router on Stick Topology is done.