- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
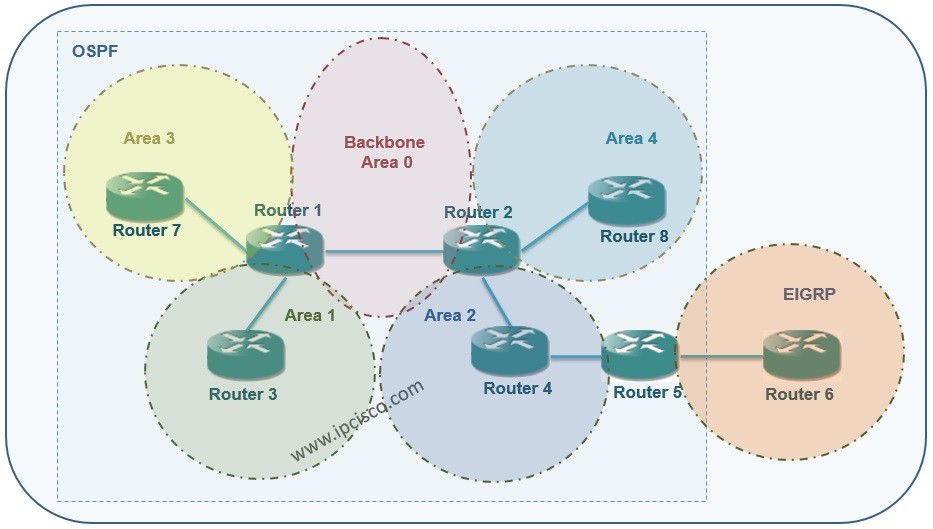
Table of Contents
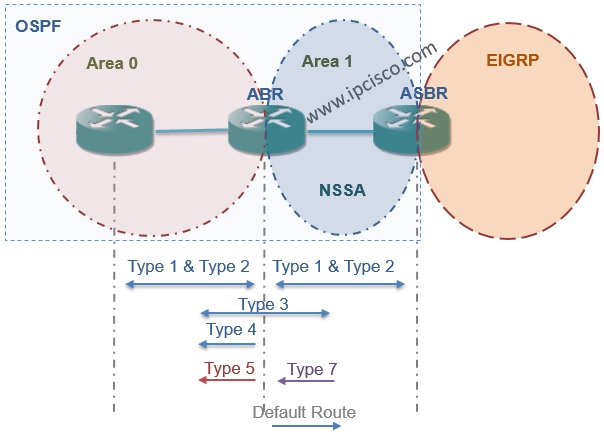
Not So Stubby Area name is the most funny name in network world, I think : ) Funny and useful. With OSPF NSSA, the External LSAs (Type 5) that is not accepted by Stub Areas, accepted as Type 7. Here, we will learn how to configure NSSA on Packet Tracer, OSPF NSSA Configuration.
Normally, NSSA are do not accept Type 5 LSAs. But it convert Type 5 to Type 7 and then accept. After NSSA, at the ABR, this convert process is done again and Type 7 LSAs is converted to Type 5 LSAs.
You can check the below lessons for the configuration of different OSPF Area Types:
The routes that is related to Type 7 LSAs, will be like N1 and N2 routes in the routing table.The difference between these two route type is explained before.
In NSSA, Summary LSA Type 3 is accepted like Stub Area. Beside, if a default-information originate command is used in ABR, default-route is also accepted.
To configure NSSA, all the routers in the area need to be configured as NSSA. This configuration is like below:
For default-route, the below command is used:
On our main topology, we will configure the Area 2 as not so stubby area (NSSA). The not so stubby area (NSSA) configuration will be like below on Router2, Router4 and Router5:
After this configuration, the show ip route output will be like below:
Here, you will see an output like stub area, but there is one difference. This difference is Type 7 LSA and External Route, N2.
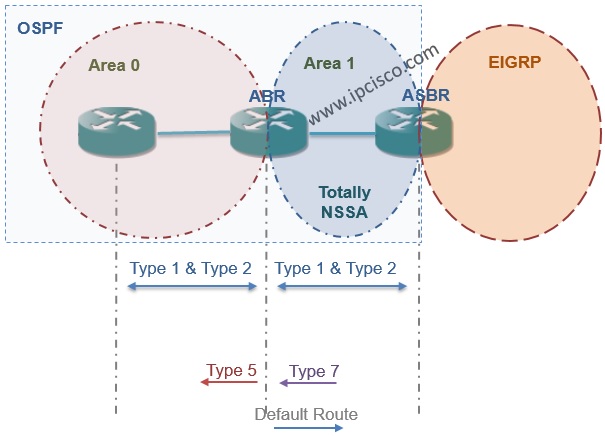
Totally Not So Stubby Area is like Not So Stubby Area except one diffference. In Totally NSSA, Summary LSAs(Type 3 and Type 4) are also not accepted. It get these with only one default route. And this is configured ar ABR by default-information-originate command.
Leave a Reply