- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
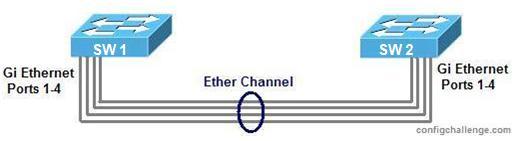
Table of Contents
Spanning-Tree blocks redundant links and avoid Layer 2 loops. Etherchannels load balance the traffic between the redundant links and uses the bandwidth more efficient. Sp, how can we configure etherchannel? To understand more clear, here is a basic Etherchannel Configuration scenario with Cisco PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol). You can check PAgP definition on wiki also. We have also done this with LACP before in another Link Aggregation example.
Here, two switches connected by four cable from their gigabit ethernet ports. We will bundle four of the physical link into one logical link.
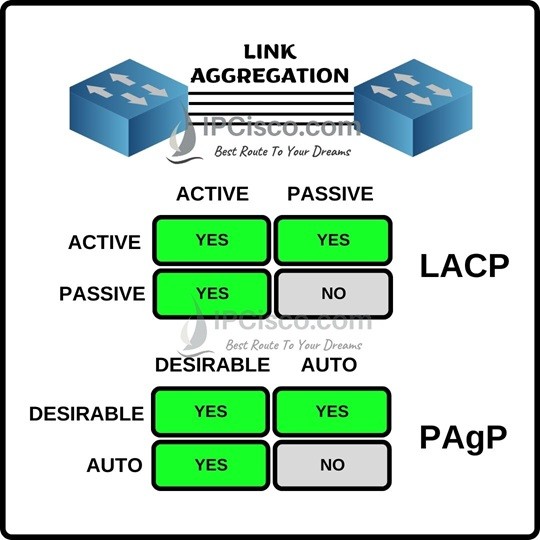
There are two different channel group mode is used in PAgP. These channel group modes are given below with also LACP modes.
According to this information, if both ends are configured as Desirable, link aggregation is established. If at least one end is configured with Desirable mode, PAgP link aggregation is again established. But, if both end is configured as Auto, then link aggregation is not established.
The similar thing isalso true for LACP with different mode names. If both ends are configured as Active, link aggregation is established. If at least one end is configured with Active mode, LACP link aggregation is again established. But, if both end is configured as Passive, then link aggregation is not established.
1. First of all, we must create logical interface with “port-channel” command and assign it an ip address. Before assigning an ip address, it is important to change this port to a Layer 3 port by “no switchport” command.
SW1 (config) # interface port-channel 1
SW1 (config-if) # no switchport
SW1 (config-if) # no shutdown
SW1 (config-if) # ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
SW1 (config-if) # end

Leave a Reply