- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
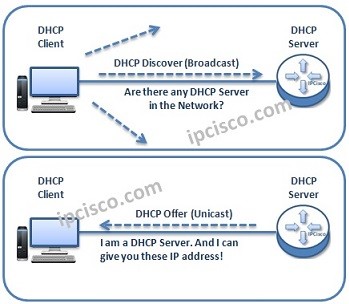
Table of Contents
DHCP does its job with Messages like many protocol. Here, as we mentined before, DHCP uses DHCP Messages. Let’s see how these DHCP Messages are used in DHCP IP Allocation Operation.
Here, firstly we will explain the main DHCP Messages for a successfulDHCP IP Allocation Operation. In this operation four DHCP Message is used.
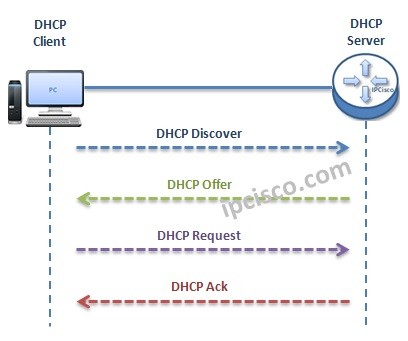
You can also learn Packet Tracer DHCP Configuration
You can watch DHCP Everview lesson also on Youtube!
For IP allocation, firstly, DHCP Client sends a Broadcast DHCP Discover Message. This DHCP Discover Messege ask this question :
There is also one more important flag in DHCP Discover Message. This flag is “Broadcast Flag”. If this flag set to “1”, this means that DHCP Client is waiting Broadcast responses from the DHCP Server. But if it set to “0”, this means that DHCP Client is waiting Unicast responses from the DHCP Sercer. Even if this flag, the DHCP Server acts as its capability. In most cases, the responses of DHCP Server is Unicast.
All the nodes in the network receive the DHCP Discover Message. But, only the DHCP Server reply to this message with DHCP Offer Message. This DHCP Offer Message is sent as Unicast or Broadcast, according to the Broadcast Flag in DHCP Discover Message and DHCP Server capability.
The meaning of this message is :
• MAC address of DHCP Client,
• IP address of DHCP Server
• MAC address of DHCP Server
• Offered IP address and Subnet Mask
When DHCP Client gets the DHCP Offer Messages, it determines one of the DHCP Server and sends a Broadcast DHCP Request Message that says, it select a DHCP Server. In this DHCP section, DHCP Client can get many offers from the different DHCP Servers. But, it selects only one of them. This is generally the first sender.
This message means that:
At this stage, accepted DHCP Server sends a DHCP Ack Message.In this messages assigned IP address and other IP informations are send to the DHCP Client. This message is again can be unicast or broadcast according to the Broadcast Flag in DHCP Discover Message and DHCP Server capability.
This message means that:
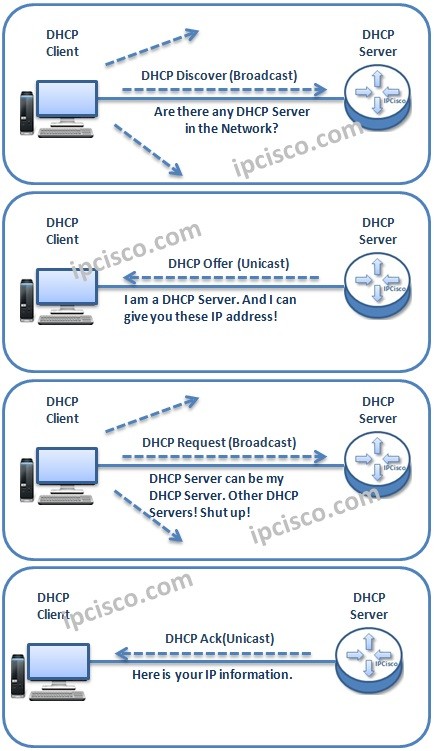
The scenario above is the scenario if everything is going good. But what if a DHCP Client request an IP addres and the requested IP address is not available in DHCP Server? At this time, DHCP Server sends a DHCP NAK Message.
This message means:
This message means:
This means that :