- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
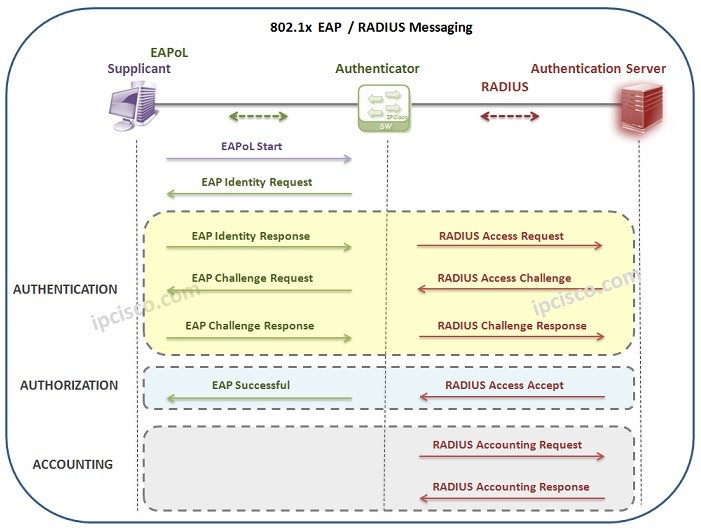
Table of Contents
For security, users needs to be authenticated in a network. For user authentication, there are various authentication methods. One of them is 802.1x Authentication. What is 802.1x? In this lesson, we will focus on IEEE 802.1x Protocol and learn the details of this authentication process. You can also check Cisco 802.1x Authentication Configuration Example.
Let’s firstly start with the question, What is 802.1x? IEEE 802.1x is a LAN Security Mechanism that provides Port Based Access Control in the network devices. With 802.1x mechanism, devices needs to be authenticated before accessing the network. Here we will focus on the details of Port Based Network Access Control.
You can also check Dynamic ARP Inspection , Switch Port Security and DHCP Snooping Mechanisms.
After learning what is 802.1x, now, it is time to learn the devices used with IEEE 802.1x Protocol. In IEEE 802.1x Authentication mechanism, there are three different devices which has different roles. So, what are these roles? These three different 802.1x devices and their roles are explained below:
Supplicant : The end point device or software that nees to be authenticated before network access. Windows, Linux, MacOS can be examples of supplicants. Here, supplicant communicates with the authenticator and sends credentials for this authentication. This is done over EAPoL.
Authenticator : Authenticator is the central point which acts according to user credentials information. It is unaware of EAP Authentication process. Authenticator takes EAP packets from supplicant and encapsulates them into RADIUS packets. Then, sends them to the Authentication server. At the end of the process, Authentication server. informs Authenticator to open the lport or not. It can be a switch, a router, an access point, a WLC or any other network device.
Authentication Server : The device that checks the supplicant’s credentials and provides authentication or not.Authentication server sends its results to the Authenticator.
Here, let’s go through an example. Think about that you are a new employee in a company and you have just get your laptop. You would like to connect the company’s network. Here, the client device that your company has given to you, is the Supplicant.
If your company is using 802.1x Authentication, it has two main configurations in the company network for network users. These configurations are done by the company IT staff to secure company network. These configurations are:
- Switch’s 802.1x Configuration (Authenticator)
- AAA Server Configuration (Authentication Server)
The company switch port that you are connected to, must be configured with 802.1x Authentication. Beside, usernames and passwords of the clients (Supplicant), must be defined in the AAA Server.
So, when you try to connect the company’s network, you need to be authenticated. This authentication is done by company’s Authentication Server through the switch (Authenticator) that you are connected to.
Here the process works like below:
- Network Connection Request to Authenticator (Switch)
- Identity Request to Supplicant (Host)
- User & Password are Sent to Authenticator (Switch)
- Authentication Check Request to Authentication Server (AAA Server)
- Authentication Server will confirm the authentication and it is sent to the Authenticator (Switch)
There is alsa an Authentication Protocol used between Supplicant (Host) and Authentication Server (AAA Server). The name of this protocol is EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) . With EAP, Supplicant and Authenticator determines the Authentication method.
Here, there are different other protocols and encapsulation technologies are used between Supplicant, Authenticator and Authentication Server.
The technology between Supplicant and Authenticator, is Ethernet, a Layer 2 technology. Here, the EAP packets are transfered in ethernet frame with EAP over LAN (EAPol) encapsulation.
The protocols used between Authenticator and Authentication Server are RADIUS or Diameter Protocols. This parts works on Layer 3.
Now, let’s think about a 802.1x process with RADIUS and check both EAP and RADIUS messages between the three components of IEEE 802.1x Protocol.
An IEEE 802.1x Authentication process can start in two ways. The first one is periodic EAP Identity requests of the Authenticator. When a new port become online, authenticator detects it and starts authentication process. The other way can be done by Client (Supplicant). Client can send EAPOL Start Message to start this authentication process. Let’s see these steps.
1) The first step of IEEE 802.1x Authenticaiton is EAPoL Start Message sent by the host to the Authenticator (Switch). It means, “I would like to enter the network”.
2) The switch (Authenticator), response with an EAP Identity Request (User & Password) to this message. It means, “Who are you?”.
3) At that time, Authentication starts. User sends its user & password information to the switch. This means, “I am A and my password is xyz”.
Leave a Reply