- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
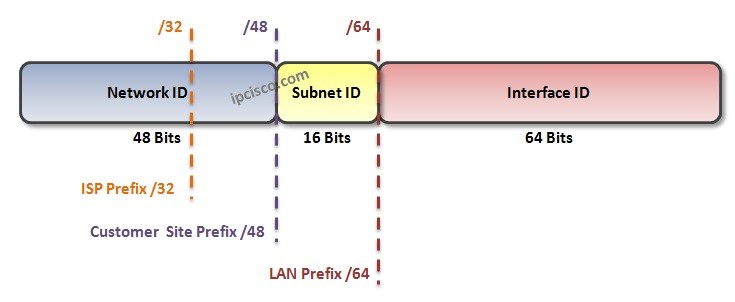
Table of Contents
We have talk about IPv4 Subnetting in another lessons. In this lesson, we will focus on IPv6 Subnetting and how to use it with IPv6 Addresses.
Subnetting is used in IPv4 to use the address spaces effectively. But IPv6 provide too much addresses. So using Subnetting with IPv6 do not aim to use only the address space effectively. Instead, it is used for the below reasons:
By the way, in IPv6 there is no Subnet Masks like we use with IPv4 Addresses. Instead of Subnet Masks, we will use Slash notation with IPv6 Addresses(like /x).
You can also check Subnetting Cheat Sheet
As you know IPv6 Addresses are 128 bits long. These 128 bits can be devided into three part and one of them is used for IPv6 Subnetting.What are these IPv6 Address parts? These parts are :
We can also divide Network ID part into two. These IPv6 Network ID parts are given below:

ISP Prefix is the part that is given to Local Internet Registries (LIRs). Customer Site Prefix is given to organizations. Organizations use Subnet bits to divide this prefix into different subnets.
In IPv6 , minimum /64 prefixes are recommented to use. This is also because Auto IP Configuration requires 64 bits. With this large prefix, we will still have a lot of IPv6 Addresses available. If you have 1 thousand devices in your network, you will still have 264 -1000 available addresses. And so, /64 addresses are also used on point-to-point links. Think about it, with IPv4, we were using /31 addresses for point-to-point links.
In IPv4, with Subnetting, Subnets and Host can be calculated and especially according to the host number, we were using Subnetting. In IPv6 , the important point is your Subnet numbers instead of the host numbers. There are too much hosts but the subnets you would like to have can be different according to your need.So, we will focus on dividing subnets and subnet numbers of IPv6 Addresses.
As we have discusses above, there are three parts in an IPv6 Address. The first 48 bits are Network bits, the 16 bits after that are Subnetting bits and the last 64 bits are Interface bits.
Here, our Subnetting bits that we will use on an address will be calculated according to our need. For example, if we have a /48 prefix and we need 8 subnets, we can use 3 subnetting bits (23=8). Our slash notation will be 48+3= 51 (/51). With this IPv6 Subnetting , we can use 8 subnets with this IPv6 Prefix. Beside, we will have (213=16384) /64s for each Subnet.
You can find the common Subnet Prefixes Table below. As the table shows for example, if you have a /56 Prefix, you can have :
if you have a /52 Prefix, you can have :
You can also test your IPv6 Knowledge on IPv6 Questions Page.
To understand IPv6 Subneeting better , let’s go through some examples and try to understand IPv6 Subnetting.
To understand IPv6 Subneeting better , let’s go through some examples and try to understand IPv6 Subnetting.
Leave a Reply