- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
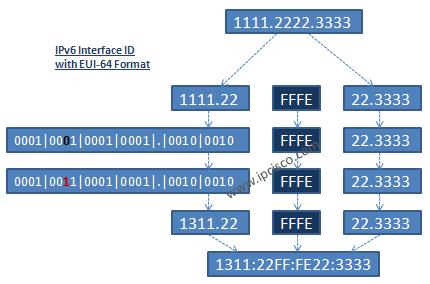
Table of Contents
IPv6 Address is the new generation IP address that is mainly developed to overcome IPv4 exhaust and its limitations. As you know, IPv4 Addresses were limited and exhaused shortly. For the new technologies, more IP addresess needed and for this need a new IP version has developed. This new Internet Protocol version is IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). We can say that, IPv6 is the new Internet Protocol version that we will use alone or beside IPv4 on our network devices anymore.
You Can Also View Full IPv6 Course.
So, what about IPv5 after IPv4? IPv5 has named as Internet Stream Protocol (ST) that has never become an official standard protocol. It is mainly developed for streaming video and voice as experimental protocol for research and development. It was providing effective data transfer on specific frequencies. It was the foundation of Voice Over IP (VoIP).
Like IPv4, IPv6 has also different IPv6 Address Types. We will talk about these address types one by one in the following IPv6 lessons detailly. Here, we will focus to the basics of this lesson. After this lesson you can also learn IPv6 Subnetting. You can also check wiki definion of IPv6.
You can also learn IPv6 Packet Tracer Configuration.
IPv4 is widespread implementation of IP protocol. It has 32 bit adress space, so it allow to use almost 232=4,294,967,296 addresses in internet. Because of the fact that these addresses has run out, a new version of IP has revealed. With this new IP version, more addresses are available. The number of these new version of ip addresses are especially mentioned as almost unlimited.
Before IPv4 addresses run out, some techniques like CIDR, NAT, Priviate Addresses are used to alleviate this shortage. But with the development of information technology, more devices has joined to the internet and they are still joining.
The new and the next generation version of IP, IPv6 has 128 bit address space. So, almost 2128 available addresses can be created with this new IP version. This is almost 340 undecilion available addresses, nearly unlimited!
With the development of this new internet protocol, some new features has also created. These are the new features that IPv6 Brings. These new benefits that comes with IPv6 are given below:
As you remember, IPv4 addresses are written with Decimal numbers. Different than IPv4, IPv6 addresses are written with hexadecimal digits. There are 10 numbers is the decimal numbering system. Beside, in Hexadecimal numbering system, there are 10 numbers and 6 letters (A, B, C, D, E, F). We can use both numbers and these letters (A, B, C, D, E, F) to create an IPv6 address.
IPv6 address consists of 8 groups (separated with colons) and in each colons, there are 4 digits. Each digit can be creatd with 4 bits. So, with these numbers, the address become 8 x 4 x 4 bit = 128 bits.
To understand the structure of an IPv6 address, let’s give an example:
2345:0425:2CA1:0000:0000:0567:5673:23b5
As you can see above, our IPv6 address has 8 groups and each group is seperated by colons. In each group, there are 4 digits. Each of these digits can be created with 4 bits. Total there are 128 bits address.
IPv6 addresses are very logn addresses, so sometimes we need to shorten these addresses. To do this we use specific abbreviatioins in IPv6 World. In other words, there are some abbreviations that are used with IPv6 address. These abbreviations are mentioned below with related IPv6 examples
During IPv6 address creation, there can be leading zeros at each groups. There is no need to write the leaing zeros in an address. Leading zeros can be dropped to shorten the address. In the below examole, we drop the leading zeros. Here,the importan point is this: Only the leading zeros an be droped. we can not drop any zero at the middle or at the end of a group.
2345:0425:2CA1:0000:0000:0567:5673:23b5 ==> 2345:425:2CA1:0000:0000:567:5673:23b5
As you can see above, instead of writing 0425, we wrote 425. Again, instead of writing 0567, we wrote 567. The zeros at the beginning of each group has dropped.
In an IPv6, a group can consist of all zeros. In such a case, we do not need to write, all the zeros in the address. Instead of it, we can write one zero that means four zeros in the group.
Below, you can find an example of this IPv6 usage.
2345:0425:2CA1:0000:0000:0567:5673:23b5 ==> 2345:0425:2CA1:0:0:0567:5673:23b5
In this address, we have used 0:0, instead of using 0000:0000.
There can be many zeros in many groups of an IPv6 address. To write all these zeros are very difficult for an IP address consist of 128 bits. To overcome this, IPv6 has a “double colon” shorten mechanims. We can use double colon to shorten continuous zeros in an address. In other words, if we have an entire field of zeros in ana address, we can use only one 0 for each colon. Here, the important point is this: We can use double colon only once in an ipv6 address.
Below, you can find an example of double colon usage with IPv6 address.
2345:0425:2CA1:0000:0000:0567:5673:23b5 ==> 2345:0425:2CA1::0567:5673:23b5
Here, instead of writing 0000:00000, we wrote ::
IPv6 addresses are consist of two different parts. These parts are given below:
Network Part is used to identify the network and used for routing. Node part is used to identify the node itself.
Beside this, we also divide network part into two. These parts are Unicast Address and Subnet ID. So, we can say that, ipv6 address consist of mainly in three parts:
IPv6 Address always use CIDR (Classless Inter Domain Routing) to determine the IPv6 Prefix. It is also used with IPv4 addresses with slash (/) and the network bits. Here, we also use this mechanism.
You can find an example of an Ipv6 Prefix with CIDR value below:
2345:425:2CA1:0000:0000:567:5673:23b5/64
IPv6 unicasts generally allocate the first 64 bits of the address to identify the prefix and the remainning 64 bits are identify the host portion. This interface ID is based on the interface’s hardware address. This interface ID can be produced by EUI-64 format for IPv6 Link Local Address.
To sum up Interface ID Creation with EUI-64 Format, assume that we have a MAC address of 11-11-22-22-33-33. Follow the steps in the below steps to produce an IPv6 Interface ID from this MAC address:
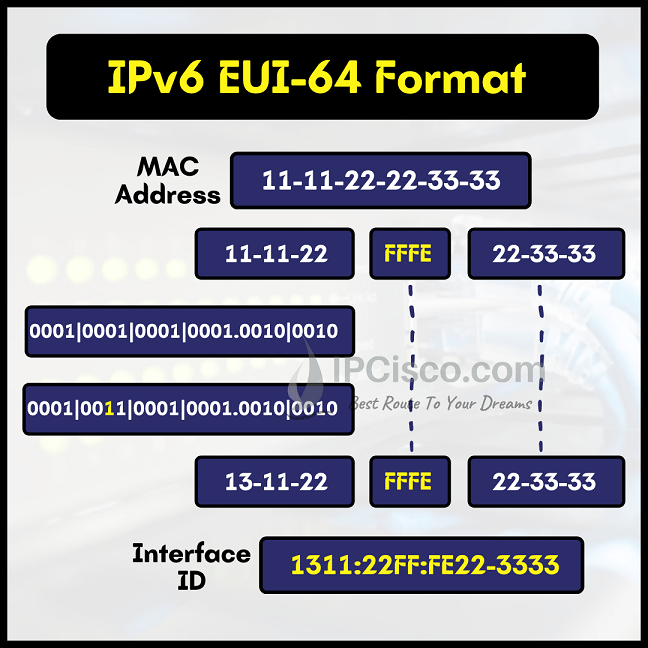
This EUI-65 Format is used for IPv6 Link Local Address Auto Address Configuration. There are various IPv6 Address Types. We will talk about these IPv6 Types and other IPv6 Examples in another lesson detailly. If you would like to learn IPv6 details, you can follow the other lessons.
a) 8 bits
b) 20 bits
c) 32 bits
d) 100 bits
e) 128 bits
a) C
b) D
c) E
d) F
e) G
a) Increased address space
b) Simplified configuration
c) Integrated security
d) Backward compatibility with IPv4
e) All of them
a) 2
b) 4
c) 8
d) 16
e) 32
a) 2266:0025::0012:0000:ad12
b) 2266:25:0:0:0:12:0000:ad12
c) 2266:25:0:0:0:12:0:ad12
d) 2266:25::12:0:ad12
e) 2266:25::12::ad12
Answers: 1)e 2)e 3)e 4)c 5)d
Leave a Reply