- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this CCNA Lesson, we will focus on routing in networking and routing tables. We will learn what is routing, what is routing table and routing table parameters one by one. We will also learn routing table Cisco router parameters one by one. So, to learn routing table details, let’s start!
Table of Contents
In networking, Routing is the process of path decision through the destination and forwarding the packets though this path. With routing process, routers decide where to send the packets. In other words, routing is one of the intelligent parts of networking. Because, according to some metrics, available paths are determined through a destination and the best path is selected between these paths.
Routing is done by routers. Every router needs to know the destinations and to know them, they need to calculate routes. Routers uses routing tables for this mechanism. So, what is a routing table?
You can test you knowledge on All Network Questions Page!
We have learned what is Routing. Now it is time to focus what is Routing Table question. Routing table is basically a data list stored in Routers. Routers stores the available routes and the best routes in this routing tables.
Routing tables are built with directly connected nodes, with static routing and with routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, EIGRP etc. With this routing information, a list is created and this list is called Routing Talbe.
In Routing Table there are different parameters that has different meanings. In a Cisco router or in a routing table Cisco view, we can see a lot of parameters related with routing decision. What are these route table parameters?
In Routing Table, there must be some parameters. These mandatory parameters are given below:
Below, you can find an example of a routing table entry and its fields.
Source Protocol is the letetr which shows sthe origin protocol of the route.
Destination Network is the network that the router can send the packet to it. Example: 192.168.0.0
Destination Subnet Mask, is the Subnet ID of the destination address. Example: 255.255.255.0
Preference (Administrative Distance) is the default value which shows the routes trust value.
Metric is any value which shows the quality of the path according to various parameters of different protocols, mechanisms. Example: 10
Next Hop, is the next node that the packet will sent on the way to the destination network. Example:192.168.0.1
Outgoing Interface, is the interface that the packet will be sent out it on the way to the destination. Example: Ethernet 0/0
Basically, we can sum up these three parameters with this sentence:
“Go to this place, by passing through this place and your link quality is this”.
You can download various Cisco Packet Tracer Labs
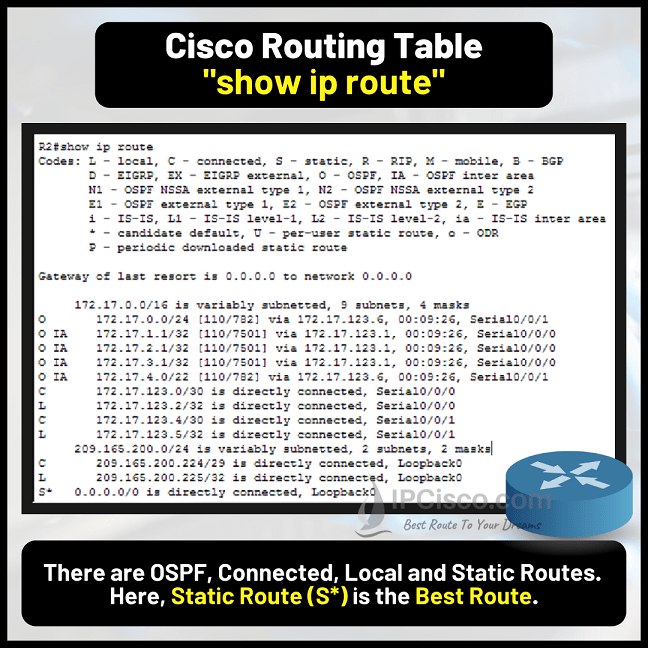
Beside the parameters of a routing table, there are some specific letters that shows important information in routing tables. These letters are used to show the routes of a specific protocol. Below, you can find the widely used letters of Cisco Routing Tables and their meanings:
By the way the best route in the routing table is showed with asterisk symbol with one of these letters. For example: *S
In this lesson, we have learned what is Routing Table and we have checked Routing Table Cisco examples to learn the details of these important data lists.
Leave a Reply