- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
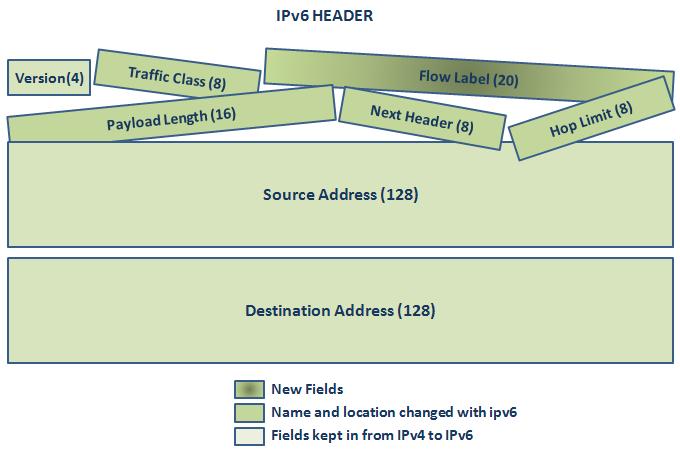
Table of Contents
IPv4 and IPv6 are the two man version of Internet Protocol, IP. Both IPv4 and IPv6 has Headers and these headers are a little different. After IPv4 Header, IPv6 Header has designed to be simpler and more efficient even it has a longer address space. In this lesson, we will see both IPv4 Header and IPv6 Header. You will find an opportunity to compare these two IP version headers.
There are similar, different and renamed fields in IPv6 Header if we compare it with IPv4 Header. In this lesson, we will see all these similarities and differences of these IP Headers.
You can also learn Packet Tracer IPv6 Configuration.
IPv6 Header has less fields if we compare it with previous version IPv4 Header. What are these IPv6 Header fields? All these Ipv6 Header fields are given below:
Now, let’s talk about the roles of these IPv6 Header fields one by one.
Version fields is a 4 bits long field that indicates the version of IP. Here, our IP version is IPv6, so the value of this field will be “6 (0110)”
Traffic Class field is a 8 bits long field that is similar to IPv4 ToS (Type of Service) field. With the help of Traffic Class, DSCP Marking is done.
The Flow Label field is 20 bits long new field in IPv6 Header. With the help of Flow Label, specific traffic flows can be tracked. IPv6 routers use this field to distinguish different traffic flows between the destination and the source.
Payload Length is 16 bits long. It is similar to IPv4 Length field. Mainly this is the length value of the data portion of IPv6 packet. The length does not include the main IPv6 Header. In IPv4 Lenght field, it includes also IPv4 Header. But in IPv6 it is not included. With this 16 bits, maximum 65,355 byte-long packets are allowed. But generallt, IPv4 and IPv6 packets are 1500 byte long. But IPv6 can carry larger packets called Jumbograms. Hıop by hop extension header is used for this purpose. A Jumbogram packet length that can be carried by IPv& packet can be between 65,536 and 4,294,967,295 bytes.
Next Header field is a 8 bits long field that is similar to IPv4 Protocol field. It shows the protocol after IPv6 header. In other words, it shows the upper layer protocol like TCP, UDP, SCTP. Some of the Next Header protocols and their Hex values are given below:
Hop Limit field is 8 bit long field similar to IPv4 TTL field. It shows the maximum allowed hop through the travel of the packet. In other words it ensures a packet circulation because of a routing loop.
Source Address field is a 128 bits long field that includes the source IPv6 address. As you know an IPv6 source address is 128 bits log as all IPv6 addresses.
Destination Address field is a 128 bits long field that includes the destination IPv6 address. As you know an IPv6 destination address is 128 bits log as all IPv6 address.
By the way, let’s also talk about the Ethernet Header for IPv6 packets. IP is encapsulated byEthernet generally. In an Ethernet Headers, there is a filed called EtherType which shows the upper layer protocol. In Ethernet II Header, if the upper protocol IPv6, in EtherType field, 0x86dd is used. If it is IPv4, in Ethertype field 0x800 is used.
You can also test your IPv6 Knowledge on IPv6 Questions Page.
IPv4 is the previous version Internet Protocol. It has more parts if we compare it with next genertation IP, IPv6. So, what are the fields used in an IPv4 Header? Below, you can find all the fields used in an IPv4 Header:
What are these IPv4 Header field’s roles? Let’s explain the roles of each IPv4 Header field one by one.
Version field is a 4 bits IP version field. It is set to 4.
Header Length
Header Length is 32 bits long and it has minimum 20 bytes and maximum 60 bytes.
ToS (Type of Service)
ToS (Type of Service) is 8 bits long field used for QoS. The first 3 bits were used for QoS as IP Precedence. Later the first 6 bits were used for QoS as DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point). The last 2 bits are used for ECN.
Total Length is the lenght of the packet. It is 16 bits long. The minimum size of an IPv4 Header is 20 bytes and the maximum size is 65535 bytes.
Indetification is the 16 bits long field that is used to differentiate fragmanted packets from different datagrams.
Flags filed is 3 bits long.It shows possible fragmentations. First bit is always 0. Secons bit is DF(Don’t Fragment), it is set to 0 if the packet will be fragmented. The last one is MF(More Fragment). If it is set to 1, it means more framentation will be done.
Fragmented offset is 13 bits long used for fragmentation or reassembly of large packets.
TTL is a 8 bits long filed that shows maximum allowed hop through the travel of the packet.
Protocol filed is 8 bits long and indicates the next protocol after IP Header.
Header Checksum is a 8 bits long field for Error Checking purpose.
Source Address field is a 32 bits long field that includes the source IPv4 address.
Destination Address field is a 32 bits long field that includes the destination IPv4 address.
Options field is a 24 bits long filed that is used for testing and debugging purposes.
Padding is a filed that provides additional 0’s to complete the IPv4 Header length as multiple of 32.
Leave a Reply