- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
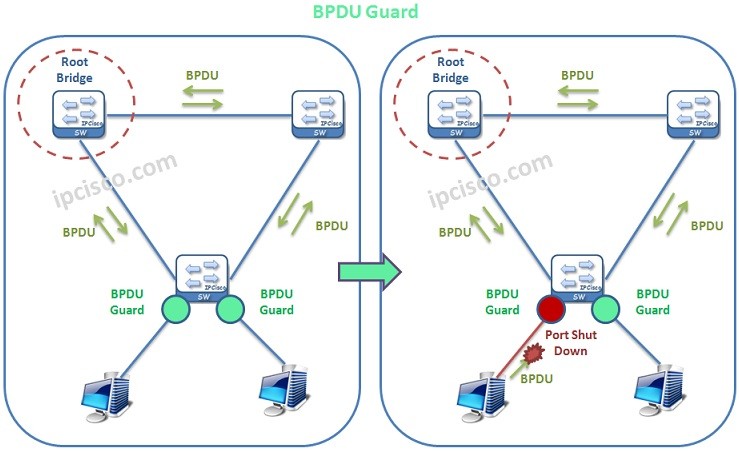
Table of Contents
The are various mechanims like BPDU Filter, BPDU Guard, Root Guard, Portfast etc. used with STP to provide stable STP topology. In this lesson, we will focus on what are these Spanning Tree Mechanims and what they do to provide a stable STP Topology. To learn about other STP Convergence Mechanism, you can visit Loop Guard | Uplink Fast | Backbone Fast | UDLD lessons.
So, what are these STP Convergence Mechanims? These STP Convergence Mechanims are given below:
Now, let’s talk about these STP Convergence Mechanims one by one detailly.
As we have discussed before, in STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) there are five port states. These Port States are :
In an STP Topology, this Layer 2 convergence time, accessing from blocking to forwarding state,is 50 seconds. These 50 seconds are spend in the states like below:
Total 50 seconds From Blocking State to Forwarding State.
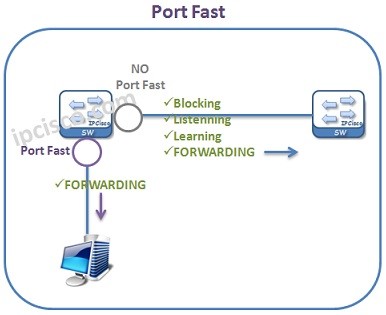
STP Portfast is used on only access ports. It is not recommended to use SP Port Fast on trunk ports. Also on the port that is connected to another switch is not recommended. Because, such a connection can cause an unaccepted Layer 2 Loop.
To configure STP Portfast Globally, you can use “spanning-tree portfast default” command globally. This will configure all switch ports with PortFast and put all the switch ports into Forwarding rapidly.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast default
To configure PortFast on a specific interface, you can use “spanning-tree portfast” under this specific interface.
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
BPDU Guard is the mechanims that protect a port towards any Bridge Protocol Data Unit. In other words, this mechanims avoid receiving BPDU packets. By doing this, BPDU Guard provide the stability of STP Topology.

BPDU Guard avoid receiving BPDU with an Error-Disabled Mode. If a BPDU Guard configured port receives a BPDU packet, it puts this port into Error-Disabled Mode.
It is configured on the related port of a Cisco switches with “spanning-tree bpduguard enabled” command.
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enabled
You can also enable BPDU Guard globally on a Cisco switch, with “spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default” command.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
BPDU Filter mechanims is used to provide also a stable Spanning Tree Protocol Topology. It avoids receiving BPDUs on the interfaces and it also provide that device not participate in STP even if it is a witch. This is useful also with Port Fast configured ports.
BPDU Filter removes Port Fast on the port, if it receives a BPDU packet. After that, it operates with normal STP.
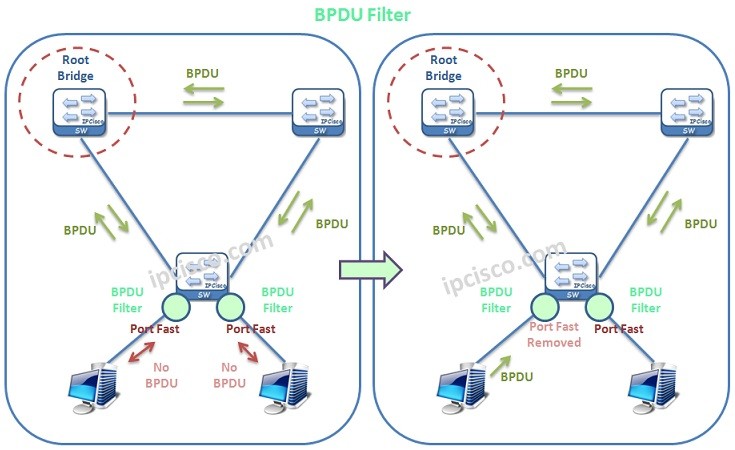
This is a little risky feature. Because if you connect a switch to a switch network this can cause a loop.
To enable BPDU Filter globally on a Cisco switch, you can use “spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default”.
Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
You can also enable BPDU Filter on a specific port. To do this, you can use “spanning-tree bpdufilter enable” command.
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
Root Guard is the Spanning Tree mechanism that prohibits an undesired switch to become a root bridge. In other words, with Root Guard, network administrators can manuplate Root Bridge selection.
Root Guard mechanims is an important mechanims that avoids Root Bridge changes in undesired times. Think about it. If a superiour BPDU comes and says that, there is a better Root Bridge. This can cause unexpected problems in a network.
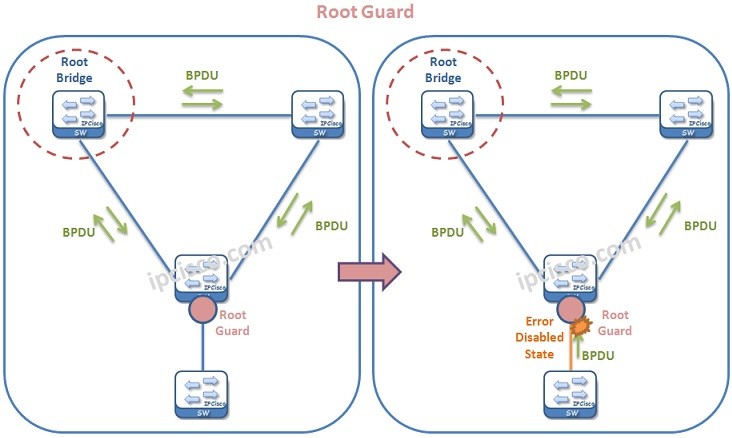
With Root Guard mechanims, STP topology and Root Bridge stay stable and unexpected problems caused by a Root Bridge change is avoided. Root Guard puts the port that received an unwanted BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit), it puts that port in an “inconsistent state”.
To configure a port with Root Guard, you can use “spanning-tree guard root” command under the related interface.
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root
To check the interfaces that is in the inconsistent state, you can use “show spanning-tree inconsistentports” command.
Switch# show spanning-tree inconsistentports
Leave a Reply