- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
In this wireless principles lesson, we will cover Antenna Types used in wireless LANS and we will learn wireless topology types like Basic Service Set (BSS), Extended Service Set (ESS), Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS).
Wireless communication is a communication type that is done over Radio Frequency (RF) Signals. As all communication types, here there is a sender and a receiver. Data can transfer through both direction as bidirectional or can only from one side to another as unidirectional. For this communication both sides of the communication must use the same frequency or in other words same channel.
Radio Frequency (RF) Spectrums and the Satellite Orbits of wireless communication are managed by International Telecommunication Union-Radio Communication Sector (ITU-R) all over the World.
Packet Tracer WLAN Configuration Example
Beside Telecommunication Union-Radio Communication Sector (ITU-R) that manages RF spectrums and satellite orbits, wireless networking standards are managed by two organization all over the World. These are IEEE and Wi-Fi Alliance. IEEE defined the technical standards of 802.11. So, network vendors produce their products according to these standards. The Wi-Fi Aliance is the non profit organization that certifies the wireless products of the vendors as they are compatible with the 802.11 standard.
Table of Contents
In wireless principles, Antennas are very important. Radio Frequencies are generated by antennas. These antennas can be located in wireless devices or can be a separate device. There are different types of antennas in wireless communication. Here, we will talk about two different types of wireless antennas.These are:
Omnidirectional Antennas receive and radiate equal power in all the horizontal directions. This can be liken to a donut. Here, around the antenna a donut shape is createw with signals. The antenna that is used by Access Points are Omnidirectional Antennas.
Omnidirectional Antennas are mainly used for point-to-multipoint configurations. Point-to-multipoint means that, they are the distributor of wireless signals and the wireless available devices receive signals from it.
Directional Antennas receive and radiate in only one direction. The strenght of directional antennas is more thanb omnidirectional antennas. You can arrange the direction of this type of anennas. Yagi Antennas are directional antennas
Directional Antennas are mainly used for point-to-point configurations. Sometimes, they can be used for point-to-multipoint configurations also.
During wireless communicaton and wireless signal distribution fort his communication, because of some factors, signals distortion occurs. In other words, different types of objects affect signals. So, which factors or which type of objects influent wireless signal distortion? These are given below:
Absorption Objects are the objects which absorb Radio Frequenct (RF) Signals. In a buildings, walls, ceilings are examples of Absorption Objects.
Scattering Objects are the objects which disperse Radio Frequenct (RF) Signals. In a room, carpets or different types of Wall paintings can be examples of Scattering Objects.
Reflection Objects are the objects which reflect Radio Frequenct (RF) Signals. Metal and glass are examples of Reflection Objects.
In wireless principles, there are different wireless topologies used. These wireless topologies are given below:
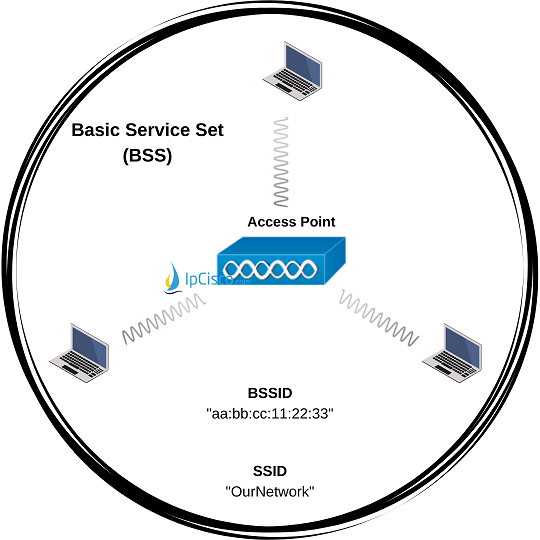
The first wireless topology of wireless principles is Basic Service Set (BSS). Basic Service Set (BSS) is a closed group of devices consist of a central wireless source and its clients that get service from this central source, that can communciate with 802.11 wireless standard. The central device can be an Access Point (AP) and the clients are the devices that are wireless capable. In other words, we can say that, BSS is a group of wireless devices served by a a single Access Point (AP). All the devices in a BSS, use the same channel to communicate.
Every BSS has a string logical name that is advertsed by Access Point. This identifier is called Service Set Identifier (SSID). In other words, SSID is the network name of BSS. It is not necessary for an SSID to be unique. But, there is another identifier that is used by devices and must be unique like and it identifies Access Point uniquely. It is the MAC address of Access Point and specifically called BSSID (ID of BSS).
Access Points use Omnidirectional Antennas. So, their signals are usable in a circle or donut like area. So, the physical borders of this area is has a specific name in wireless standard. This is Basic Service Area (BSA).
As we have talked about before, in a BSS, there is an Access Point and connected clients to this Access Point. Here, a client must be accepted by the Access point to get service from it. Firstly client sends an association request to the AP and then AP replies that it accepts this request. By doing this, association is established. If AP do not accept, then the device can not be a client of this BSS.
Communication between the devices in BSS can be done over Access Point. All the traffic pass through AP and this provide a security mechanims by managing the traffic on a central node. But, the signals are over the air, so without an encryption it is not secure. So, various wireless encryption methods are used.
Clients can communicate in the BSS. What if they would like to communicate outside this BSS. Fort his, Access Point is used. Access Points has also uplinks to the outside of the BSS with Ethernet. Though this link, clients can communciate with outside of BSS. This process is called Distribution System (DS) in wireless 802.11 standard.
Normally without VLAN configuration, one SSID is used by a single VLAN. But we can extend this for multiple VLANs with multiple SSIDs. Here, VLANs and SSIDs are different but the coverage area of the BSS is sam efor each network. Because the physical device, Access Point is the same device. Fort his type of network, different BSSIDs are used and in Cisco, this BSSIDs are determined by incrementing the last digit of the radios’s MAC address.
Access Points are limited devices. They can cover a BSA and it is called a Cell. But in many companies network area is very large that only one Access Point can not cover all the area. So, additional Access Points are used to cover all the area. This Access Points are connected through an Ethernet Switch and they become a single continuous and seamless connection from the client perspective. User can go from one cell to another without conenction interrupt. So, combining one more Access Point in a swithed network is called Extended Service Set (ESS).
In a network that has multiple Access Points, all SSIDs must be defined on each Access Point for seamless and continuous connection. Here, each Access Point’s BSSID is different but SSIDs are same.
Passing from one AP to another is called roaming. This is simply, similar logic with Mobile Operator roaming. If a client change BSA, then check for a new AP and if finds then connected to this new AP.
In 802.11 Standard, clients can directly communicate together without any need to an Access Point. This type of wireless communciation is callled Independent Basic service Set (IBSS). Another name of this is ad hoc network. Such wierless connection is used generally whenever two laptop want to share information, a PC want top rint someting from a printer etc.
For Independent Basic Service Set operation, one device works as leader. The other become client. So, the leader device advertise the network and the other want to joinm this network.
In this lesson we have covered wireless principles. We have learned wireless topology types like BSS, ESS, IBSS, beside antanna types used in wireless.
great read and very informative. thank you
might want to check for typos in the article
always weclome dr ragoo :) Good luck!
Great article, it not only explains common terms, it also sheds some light on the basics behind roaming.
Thank you Joel;) You can check also roaming types lesson to learn more on wireless roaming.