- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Layer 2 and layer 3 Switches are the main network devices that we use in networking. In this CCNA Lesson, we will focus on what is layer 2 switch, what is layer 3 switch (multilayer switch) and why we use these devices in networking. We will also compare layer 2 vs layer 3 switch and learn the differences of these two types of switches.
Basically layer 2 switches are layer 2 capable switches and they work on OSI Layer 2. Layer 3 switches or Multilayer switches work on layer 2 and layer 3 capable and works both OSI layer 2 and layer 3. In both switch types, we can use layer 2 functionalities, VLANs, Spanning Tree Protocol etc. But in only layer 3 switches, we can use Routing functionalities, Routing protocols etc.
Before layer 2 versus layer 3 switch comparison, let’s start with the definitions of these different types of network switches.
Test Yourself With CCNA Practice Test!
Table of Contents
Layer 2 switches are the traditional network switches which works on layer 2, data-link layer of OSI Reference Model. These traditional types of switches do the packet forwarding based on physical addresses, MAC addresses (Media Access Control addresses).
In almost all networks, network engineers use layer 2 switches. Because they are cheap and easy to use in networking. With a basic networking knowledge and configuration practice, a network engineer can manage a layer 2 switch.
If you have many hosts in a network and you need to connect each of this host devices to the network, layer 2 switch can be a good choice for you. Because they are the most efficient network device in a local area network.
With layer 2 switches, we can divide large networks into smaller pieces. In other words, we can divide one large collision domain into multiple collision domains.

Cisco Layer 2 Switch Examples
Collision domain is a term used in networking to imply a part of a network in which collision occurs. In a collision domain, only one device can send or receive packets at a time. If one more device sends packet at the same time in a collision domain, collision occurs.
With layer 2 switches, we can divide one collision domain into multiple collision domains. Each port of a switch is one collision domain in networking. At a time, only one device can send and receive data in a switch port. If one more device tries to send data, collision occurs.
In networking, we use layer 2 switches almost in all networks. The main purpose of these networking devices are dividing networks into multiple collusion domains and provide port density in the network. You can have many device in your local area network and you can need ports to connect these devices in the same network. At this time, layer 2 switches does this job. They provide an efficient network.
You can also use VLANs in switches and you can divide your local area network into segments. Different departments in a company can use these different segments and network efficiency beside network security is provided.
Layer 2 switches provide high speed forwarding. These network devices are used also in networks for fast data transmission.
Before going to the layer 2 vs layer 3 switch, let’s also explain what is a layer 3 switch and why we use this types of switches.
There are many benefits of layer 2 switches. First of all they are faster than routers. This provides a fast data transmission in a local area network.
Secondly, Layer 2 switches does hardware-based bridging.
Thirdly, the cost of these devices are very low if you compare with other network devices. They are cost effective devices.
The latency in a layer 2 switch is very low if you compare it with other devices.
Layer 3 switches are also known as multi-layer switches in networking. They are the switches which perform both layer 2 switching and layer 3 routing. Layer 3 switches work on both layer 2 and layer 3 of OSI Reference Model. In other words, they work in both Data Link and Network layers of OSI Model. This is the main difference of layer 2 vs layer 3 switch if we compare these switches.
Layer 3 switches use both MAC addresses and IP addresses. Because they both perform layer 2 forwarding and layer 3 routing as dynamic routing or static routing. If you use VLANs, they perform also Inter VLAN routing between different Virtual LANs.
Layer 3 devices provide more features than layer 2 switches. For example, they can provide enhanced security features, VLAN tagging based on IPs etc.
Layer 3 switches also divide networks into multiple broadcast domains.

Cisco Layer 3 Switch Examples
A broadcast domain is a logical network division in which all the devices can receive or send broadcast each other. This is done in the layer 2 of OSI model, in data link layer.
With a layer 3 switch, we can divide our network into multiple broadcast domains. And this is one of the benefits of using multilayer switches.
We use layer 3 switches for various purposes in a network. One of them is providing isolated broadcast domains in a network. Each port of a layer 3 switch is a broadcast domain. With multiple ports, we can provide multiple isolated networks via multilayer switches.
We also use layer 3 switches like routers. We can use routing protocols for dynamic routing or we can define manual static routes. Some vendors, use these enhanced switches on the edge parts of service provider networks. They are very efficient on these areas.
With layer 3 switches, we can also use policy-based routing. With this feature, we can differentiate different traffics and behave different to these traffic types according to their protocol type, ip address etc.
Layer 3 functionality of a switch can be in two forms. These are:
In, Cut-through method, only the first packet series are looked for ip address determination. The remaining packets are shifted to the MAC address. This provides higher data throughput.
In Packet-by-packet method, each packet is looked for ip address determination. They have the router functionality for routing.
There are many benefits of using multilayer switches. The first one is it provides routing functionality for both networks and VLANs.
Secondly, by dividing network into multiple broadcast domains, it reduces broadcast traffic.
Again, with multiple broadcast domains, it provides additional security and isolation of the different departments.
Troubleshooting is simple in layer 3 switches. This makes them easy to use.
The network latency is low with layer 3 switches.
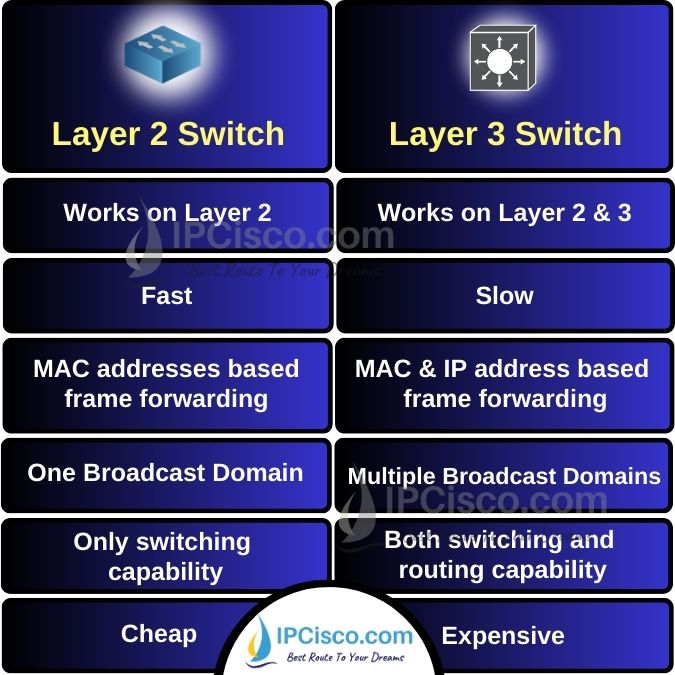
We have talked about what is layer 2 switch and layer 3 switch and we have learned why we use these switch types. Now, let’s compare layer 2 vs layer 3 switch and learn the details of these differences on a table.
The first difference on layer 2 vs layer 3 switch is the part of network that they work. Layer 2 switches work on layer 2 of OSI Model, in other words, they work in Data-Link layer. On the other hand, layer 3 switches work both on layer 2 and layer 3 of OSI Reference Model. These are data-Link layer and network layer.

Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch
Secondly, the key difference is about the speed of these switches. Layer 2 switches are faster than layer 3 switches. The forwarding mechanism is in wire-speed, so, they are faster than multilayer switches. In other words, a layer 2 switch does not examine data packets before sending them to the destination. So, it does not waste more time as layer 3 switch.
Another difference is about frame transmission if we compare layer 2 vs later 3 switch. Layer 2 switches forward frames to the destination based on MAC addresses, physical addresses. Layer 3 switches also use this layer 2 mechanism but it also routes packets based on ip addresses, logical addresses.
A layer 2 switch is only a traditional simple switch. So, it has only one broadcast domain by default. It has multiple collision domains as the number of its port numbers. On the other hand, a layer 3 switch can be multiple broadcast domains because its ports can be used as router ports. There are also multiple collision domains in layer 3 switch.
With only layer 2 capability, you can only communicate inside your network with a layer 2 switch. But if you are using layer 3 switch, you can communicate with the world outside, on internet. This is because, layer 2 switches are capable of switching only while layer 3 switches are capable of both switching and routing.
Another difference on layer 2 switch vs layer 3 is about the cost. Simple switches are very cost effective, because they are cheap if we compare its role in a network. On the other hand, multilayer switches are expensive devices because they have enhanced switching and routing capabilities.
To learn how to configure switches, you can start Packet Tracer Switch & Router Configuration Course!
Leave a Reply