- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
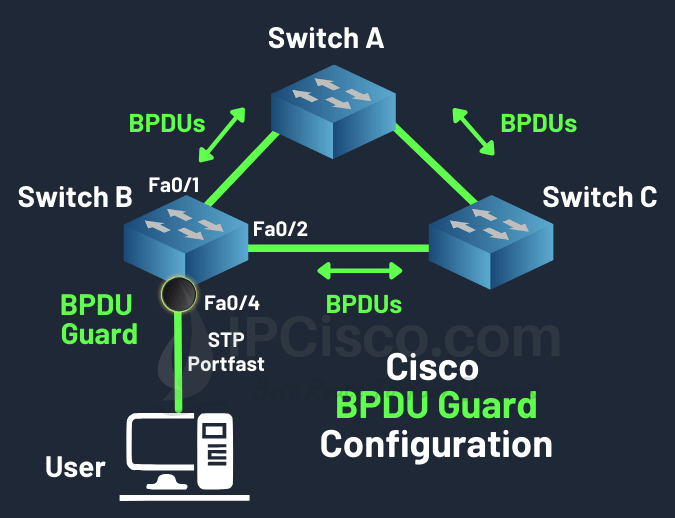
STP BPDU Guard is one of the Spanning Tree Protocol features, which is used to prevent receiving BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit). In this lesson, we will focus on what is BPDU Guard, how can we do BPDU Guard Cisco Configuration and the difference between BPDU Guard and Root Guard.
This lesson is in one of the new topics of Cisco CCNA 200-301 v1.1. This new CCNA topic is Root Guard, Loop Guard, BPDU Filter and BPDU Guard.
STP BPDU Guard is a safety mechanism that shuts down ports configured with STP portfast upon receipt of a Bridge Protocol Data Unit. Assuming that all access ports have portfast enabled, this ensures that a loop cannot accidentally be created if an unauthorized switch is added to a topology.
Table of Contents
BPDU Guard is basically an STP feature for switch safety. It is used on switch ports configured with STP Portfast towards hosts. This STP feature is used to prevent receiving any BPDU on access ports. When it received a Bridge Protocol Data Unit on this port, it shutdown the port.

STP BPDU Guard
Spanning Tree protocol uses BPDUs, so, why we need to avoid receiving BPDU? In some cases, especially on the ports that are connected to the user access ports, we need to avoid undesired switch connections. So, we prevent BPDUs to ensure that, there is no new switch coming towards that port.
What happens if a Bridge Protocol Data Unit is received from the port that is configured with BPDU Guard? At this time, that port goes to error disabled mode. And the new switch that send this Bridge Data Unit Protocolcan not access this port that we configure for BPDU Guard.
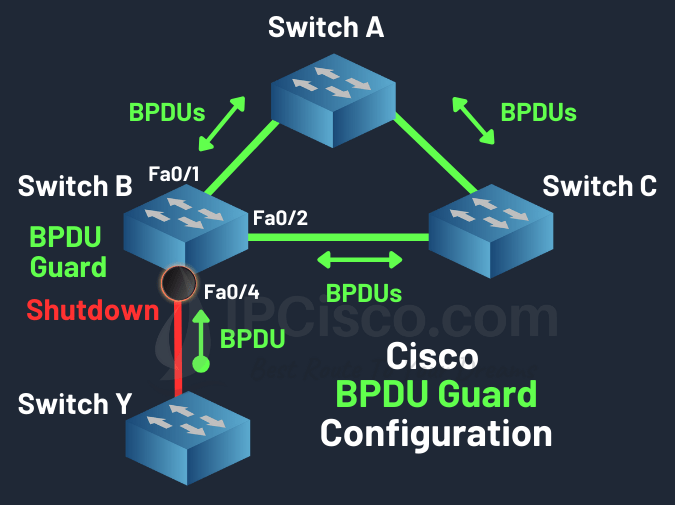
STP BPDU Guard, Shutdown Port
BPDU guard and Root guard are sometimes confused. These spanning tree protocol security features have similarities and differences. Both of these STP features prevent the same thing, BPDU, but with a difference. Root Guard prevents only receiving superior BPDU not to effect STP Root bridge. On the other hand, BPDU Guard prevents any Bridge Protocol Data Unit coming to that port. It prevents switches to connect that port.
While we use root guard on the ports towards switches, BPDU guard is used on the access ports that we do not want any connected switch.
BPDU guard and BPDU Filter are also sometimes confused. BPDU Guard is used towards access ports to prevent any switch connection to that port. It prevents receiving any BPDUs. On the other hand, BPDU filter completely prevents BPDU transmission on that port. It is used to prevent any switch to participate in spanning tree to prevent STP loops. In other words, it prevents some part of the network from Bridge Data Unit Protocol effects of a switch.
Another difference is, while the port configured with BPDU Guard can receive BPDU and after that it immediately shuts down the port. But BPDU Filter is completely prevents BPDU transfers on that port. If it receives any Bridge Protocol Data Unit, it disables filtering and changes from port-fast mode to normal port.
On Cisco switches, we can configure BPDU Guard in two ways. One of them is the global configuration for all switch ports. The other is interface configuration. Let’s firstly shows the global configuration.
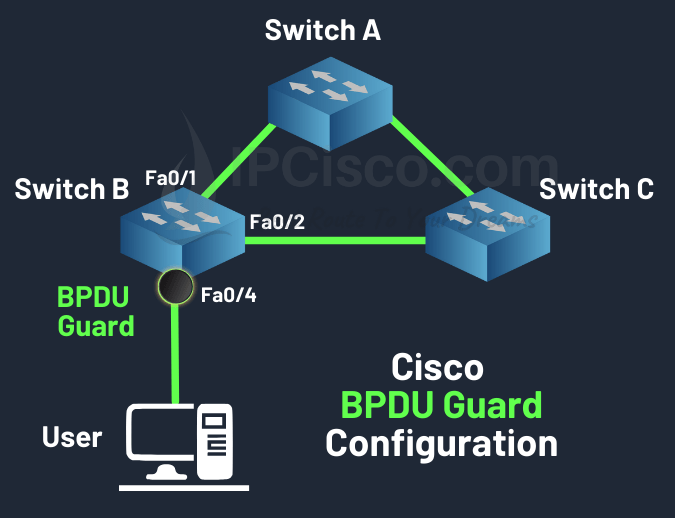
Cisco STP BPDU Guard Configuration Example
To enable BPDU Guard on a Cisco switch globally, we use “spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default” command. After that, we can disable specific ports one by one with spanning-tree bpduguard {enable | disable} command.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
To enable BPDU Guard on a Cisco switch interface, we use “spanning-tree bpduguard enabled” command. For the below example, we can configure BPDU Guard on Switch B fast ethernet 0/4. By doing this, we prevent any switch connection to this port.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface fastethernet 0/4
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enabled
To verify this configuration, we can use “show spanning-tree interface fastethernet 0/4 detail” command. The output will give also the information about this configuration.
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fa0/4 detail
Port 4 (FastEthernet0/4) of VLAN001 is designated forwarding
Port path cost 5, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.4.
Designated root has priority 32778, address 0012.aabb.4400
Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 0012.aabb.4400
Designated port id is 128.4, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
The port is in the portfast mode
Link type is point-to-point by default
Bpdu guard is enabled
BPDU: sent 16369, received 0
If a switch is connected to this port, the port is placed to ErrDisabled mode. The syslog message below will also appears.
10:33:01.025: %SPANTREE-2-BLOCK_BPDUGUARD: Received BPDU on port FastEthernet0/4 with BPDU Guard enabled. Disabling port.
10:33:01.032: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: bpduguard error detected on Fat0/4,
putting Fat0/4 in err-disable state
10:33:01.039: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/4, changed state to down
10:33:01.045: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/4, changed
state to down
To see port status, we can use “show interfaces status” command.
Switch# show interfaces status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Fa0/4 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
Leave a Reply