- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
STP Root Guard is one of the Spanning Tree Protocol features used to prevent any switch to become root bridge by sending superior BPDUs. In this lesson, we will learn what is root guard, how it works and Cisco Root Guard Configuration with an example.
You can also view other Spanning Tree Features below:
portfast | root-guard | bpdu-filter | bpdu-guard and loop guard | uplink-fast | backbone-fast | udld
Table of Contents
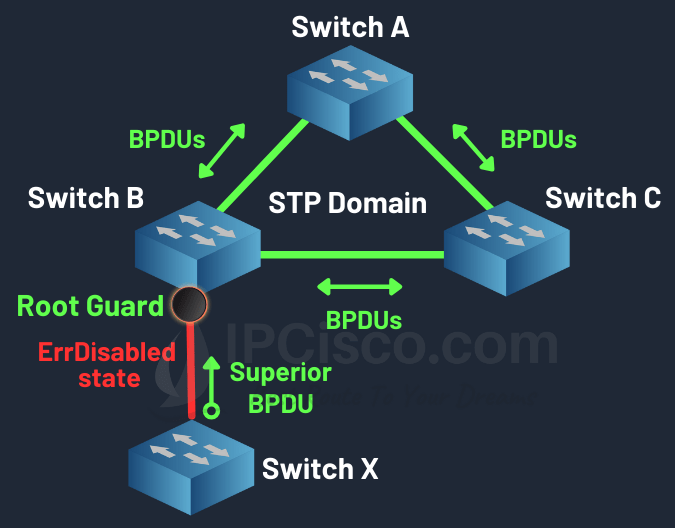
Root Guard is basically an STP mechanism which prevents any switch to become new root bridge of STP domain. Switch sends superior BPDUs and this makes them new root bridge. But with Root Guard, this is prevented. Switch can participate in STP but cannot send a superior BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit). With superior BPDU, new switch trying to say that, it is a better root bridge. But this is not true always and even if it is true, sometimes you do not want that switch to become a root bridge.
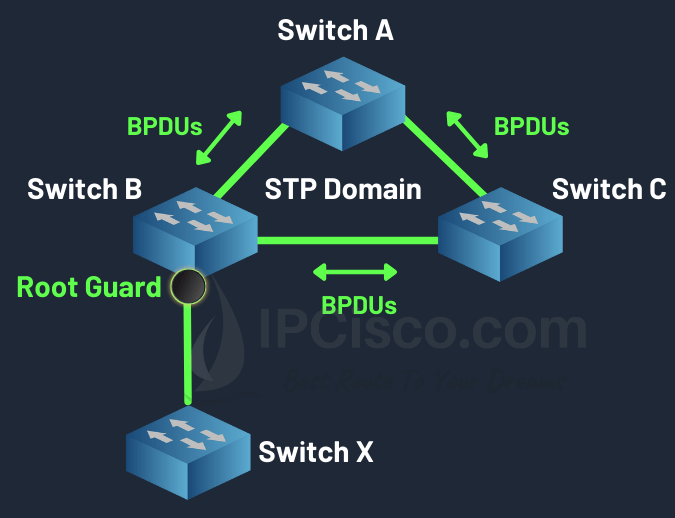
STP Root Guard
If you configure a port with Root Guard towards any switch, whenever a superior BPDU comes from that switch, port goes ErrDisabled state. This superior BPDU can be from any rogue switch or a switch that you do not want to see as root bridge. So, you use STP Root Guard feature to prevent this situation. In other words, you manage root bridge elections.

Root Guard, Errdisabled State
How to configure Root Guard on Cisco switches? Let’s learn Cisco Root Guard configuration with an example.
Root guard and BPDU guard seem similar but they have differences. If we compare Root Guard vs BPDU guard, the first difference is about their usage aim.
We use root guard not to prevent a switch participate in STP, but we use it to prevent a switch to become a root bridge. In other words, if we configure a port towards a switch with root guard, that switch can participate in spanning tree. But it cannot send superior BPDU to become a new root bridge. But when we configure BPDU Guard on the same port, it prevents any BPDU coming from that port. If any BPDU comes from this port, from the switch, it puts the port in errdisable state.
Root guard is mainly used towards the switches that should not be a root bridge. So, switches can be connected to these ports, but they cannot be root bridge. BPDU guard is mainly used towards user access ports and prevents any unauthorized switch to connect from that port.
This is mainly the comparison of Root Guard vs BPDU guard.
Cisco root guard configuration is very easy. To configure a port with stp root guard, we use “spanning-tree guard root” command under that interface.
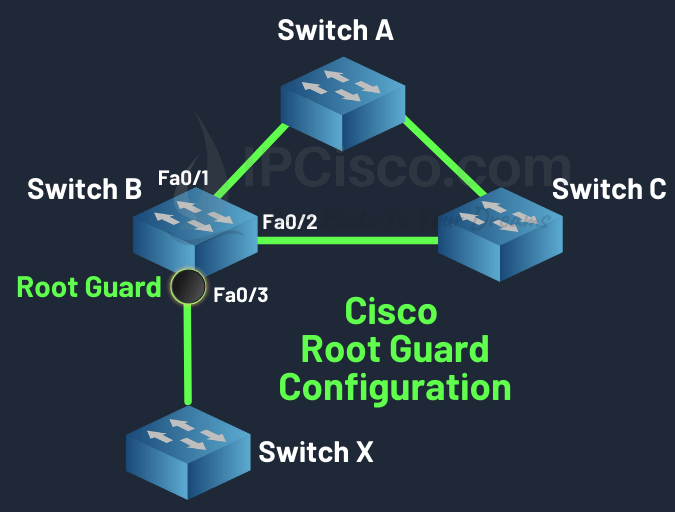
Cisco STP Root Guard Example
Here, we would like to prevent Switch X to become root bridge. So, we will configure Switch B interface towards switch X with Root Guard. This is interface fast ethernet 0/3.
Switch B# config terminal
Switch B(config)# interface fastethernet 0/3
Switch B(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root
After this configuration, whenever a superior BPDU comes from switch X to switch B ‘s fast ethernet 0/3 interface, the port will go to inconsistent state To see this you can use “show spanning-tree inconsistentports” command.
Switch B # show spanning-tree inconsistentports
There are other Spanning Tree features used for different purposes. You can also check these STP features to learn spanning tree preventation mechanism better.
You can also view, Cisco Packet Tracer STP Configuration Example!
Leave a Reply