- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
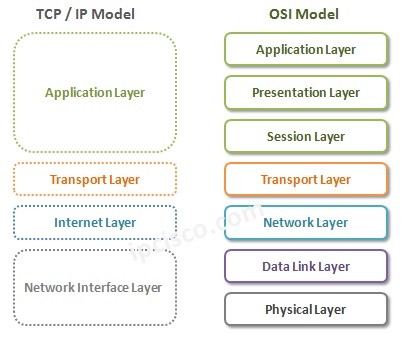
Table of Contents
TCPIP Model is another important referance model beside OSI Model in network world. OSI Referance Model was Seven Layered model, TCP/IP Model is Four Layered or Five Layered Model. The four layer model is old one. The new one is five layered tcpip model. In common, they model the same thing. But, borders of the layers of different models are different.
Let’s start with the history of TCP/IP Model and learn why was TCP/IP Reference Model developed.
TCP/IP Model was developed by U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s. It was designed by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn to create a robust and adaptable communication system that could survive network failures. TCP/IP model, originally implemented for ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), the earliest version of the Internet. In other words TCPIP is the foundational protocol suite of ARPANET which is the anchestor of today’s global Internet.
The development of TCPIP model has started to provide reliable communication between computer systems within a large area. At this part, TCP/IP model has provided a standard for this communication with its layered architecture. With this layered architecture, implementation, management and trubleshooting of networks are easier.
You can learn TCP/IP Model detailly with our TCP/IP Lesson:
There are two different TCP/IP Models which can be confused by netwwork engineers. But do not worry! Here, we will solve this problem easily. 4 layered model is the old version and the 5 layered version is the new version.
The old Four Layered TCP/IP Model has 4 layers. These layers are:
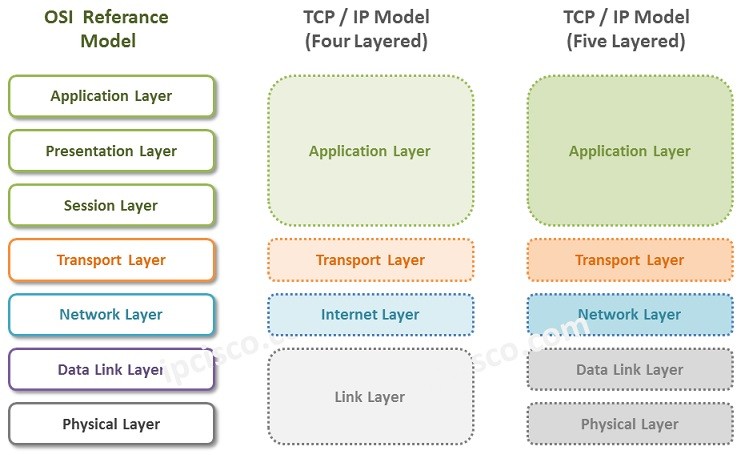
You can find the layer comparison of Four Layered, Five Layered TCP IP Model versus OSI Model below:
Let’s check Five Layered TCPIP Model Layers one by one.
Physical Layer is the First Layer of TCPIP Model. The transmission of bits, network cabling is in the responsibility of this Layer. Here, the specifications of cables an cable connectors are very important.
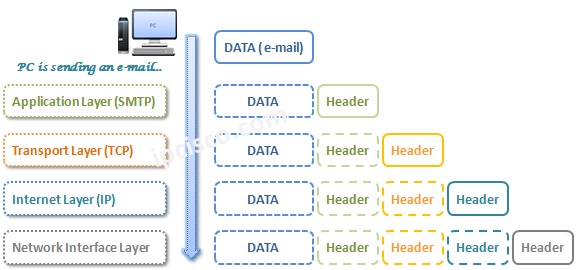
The Data Link layer is responsible for creating the frames that move across the network. The packets are encapsulated by by these frames. MAC address is used to identify the source and destination address here.
The Data Link layer protocols of TCP IP Model are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, Frame Relay, X.25, RS-232 etc. The most common protocol usedin this layer is Ethernet.
The data is transmitted and routed between the source and the destination by the help of this Internet Layer of TCP/IP Model. Internet Layer packs data into data packets known as IP Datagrams, This IP Datagrams contains Source and Destination Addresses. The main protocols used in Internet Layer are IP(Internet Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol), ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol), IGMP(Internet Group Management Protocol) etc.
Transport Layer provides the Session between end points. It manages the Sessions. Two common Transport Protocols are in this layer like OSI Transport Layer. These Trasport Layer Protocols are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Application Layer defines the Application Layer Protocols and it is the Interface between the user and the Transport Layer. It summarizes the processes that make data intended for the Application. The Protocols used in this Layer are HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), DNS, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), Telnet, TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) etc.
As you see, the Protocols used in a network is the same. Only the Referance Model and its Layers are changing theorically.
TCPIP Model combines some of the Layers of OSI and behave like one Layer. Instead of OSI Physical Layer (Layer 1) and Data-Link Layer (Layer 2), TCP IP Model use Network Interface (Network Access) Layer. Network Layer of OSI is changed as Internet Layer in TCP/IP Model. The Transport Layer is the same as OSI Referance Model. Lastly, TCP IP Model mix the three Upper Layers of OSI Model, into one Application Layer.

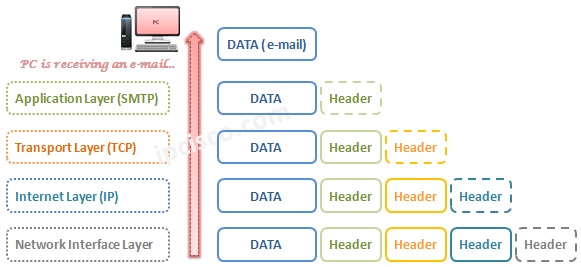
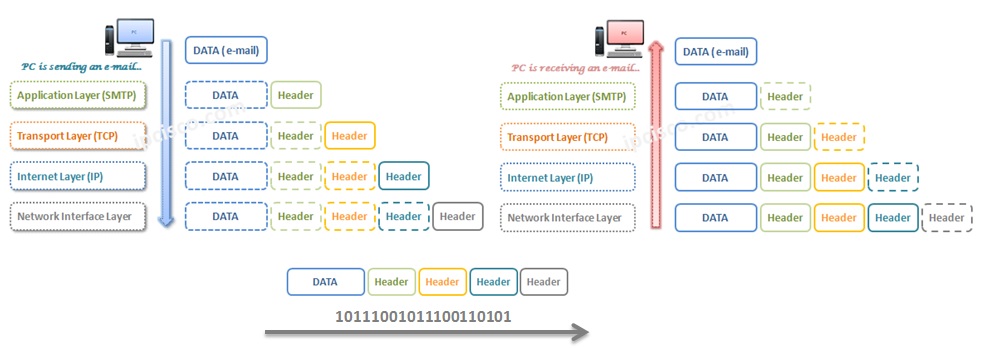
Let’s look at these picture from one end to another end. Let’s think about that, a user in a network wants to send an eMail to the other user in another network. How will the data process?
Do you have a free trial of the CCNA 200-301 package?
Unfortunatelly No Nasser. We have Blue, Silver anfd Gold Memberships.