- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the main protocol of Network Management. With SNMP, network devices are easily managed and controlled by a central mechanism. It is an Application Layer Protocol of OSI Model that provide the messaging between the controlled device and the management system. In this lesson, we will focus SNMP Overview, SNMP Ports, SNMP versions and more. We will also talk about Cisco SNMP Configuration in other lessons.
Table of Contents
What does SNMP stand for? Simply, Simple Network Management Protocol is a network monitoring and management protocol in IP networking. In other words, it is the standard protocol of network device management. With a Network Management System, we can manage network devices like routers, switches, PCs etc., we can measure device performance, we can troubleshoot network errors and we can manage next level growth of the network easily. For all these actions, Network Management System uses SNMP.
Simple Network Management Protocol is an Application Layer protocol of OSI Reference Model. In other words, it is a OSI layer 7 protocol like FTP, HTTP, POP3, SMTP etc.
In Network Management there are some terms called SNMP terms which are used with this protocol. These terms are:

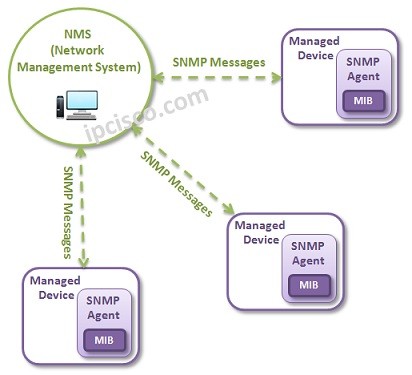
Firstly, we can talk about NMS. NMS is the Network Management System that manages the SNMP Operations and by doing this controls the Managed devices. The network monitoring and controling facilities is done here. This can be a dedicated device or an application on any device.
Second important term about Simple Network Management Protocol is Managed Devices. Managed Devices are the nodes that will be managed and controlled by Network Management System (NMS).
Then, SNMP Agent is the software part of the managed device. It collects the information for the device and reports to the NMS (SNMP Manager).
Beside, MIB is the storage database for the network management information. It contains the managed device information.
We use SNMP Protocol in Network Management. It runs on IP and UDP. IT provides different message exchange during the operations. SNMP has three versions.
Lastly, SNMP Ports, arethe ports that are used for the SNMP Communication. By default UDP Port 161 and UDP Port 162 are used as SNMP Ports.
Simple Network Management Protocol uses UDP Port 161 by default. SNMP sends and receives requests on UDP port 161. It uses also UDP Port 162 for getting SNMP TRAP⁄INFOR messages from managed devices. In other words, SNMP Manager sends commands to SNMP Agents and receives from it over UDP Port 161. If an SNMP Agent responds to the SNMP Manager with traps and information it uses UDP Port 162.
Simple Network Management Protocol can also run over TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
As other Network Protocols, SNMP has also some versions. For now, Simple Network Management Protocol has three versions. These versions are :
SNMP v1 is the first SNMP version. Only requires a plain-text community string for packet authentication and restrict access. In other words, SNMPv1 uses read-write and read-only community strings. This type of usage is vulnerable to network attacks because there is no encryption in data transfer. Basically, it has performance and security limitations. It is described in RFC 1157.
SNMP v2c is the second and widely used SNMP version. It solves the limitation fo SNMPv1 and provide more performance and efficient error handling. SNMPv2c uses read-write and read-only SNMP community strings. With read-only, it allows to reach Management Information Base (MIB) objects read only and with read-write community strings, users can edit and can do changes like configuration changes. It is more secure than version 1 but not secure than version 3. SNMv2c is also vulnerable to attacks. Additionally, SNMPv2 has more packet types than version 1. It is described in RFC 1441 and RFC 1901.
SNMP v3 is the last version and it mainly concentrate on Security issue. Adds encryption and authentication mechanism to the SNMP Messages, it do not use community strings. SNMP v3 allows a full encrypted data transmission and overcome previous version’s vulnerabilities. By doing this, as the lates version of snmp, it improves privacy. SNMP v3 has also a different message format. It is described in RFC 3410.
Below you can find a comparison table: SNMPv1 vs SNMPv2c vs SMPv3
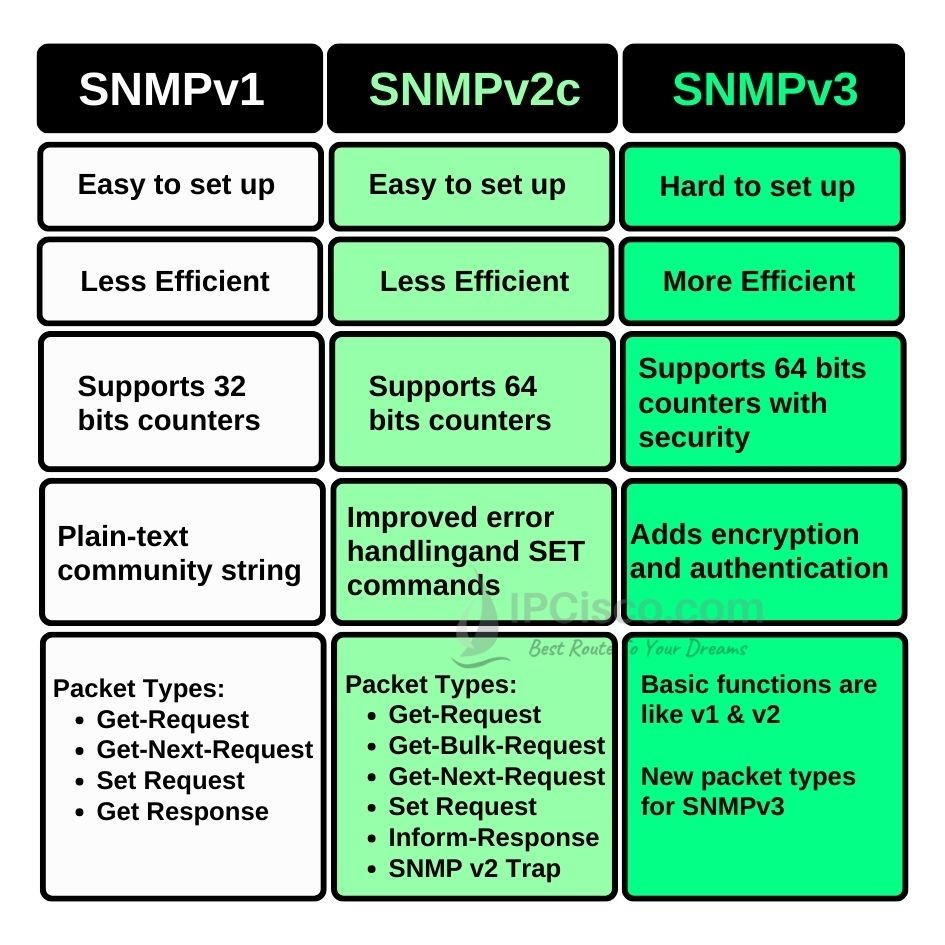
SNMPv1 vs SNMPv2c vs SNMPv3
SNMP has different packet types in different versions. Here, mainly we will focus SNMPv2c Packets. Because it has more packets than SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c is widely used. SNMPv3 has different message types than SNMPv2c.
Mainly, there are six different SNMPv2c Packets. These packets are used in SNMPv2 Operation. Each of these packets has different duty on the Network Managemeny System Architecture. Let’s see these packets and their duties detailly.
The main six SNMPv2c Packets (or Commands) are :
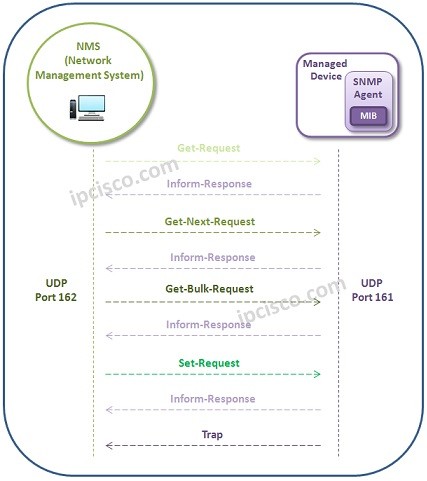
get-request : It is used to request values from Agent MIB.
get-next-request : It is used to request next MIB value from Agent MIB.
inform-response : It is the response from the Agent.
set-request : It is used to set a value in Agent’s MIB.
snmpv2 trap : It is used to inform about unusual situations.
get-bulk-request : It is used to request big data from Agent MIB.
SNMP Agents send SNMP Notifications although there is no request from the SNMP Manager. There are two types notification. The first one is Traps and the second one is Inform requests.
Traps informs the SNMP Manager about the network conditions. Inform requests are also traps but they includes request for receipt confirmation. Inform requests are more reliable than traps. However, traps are often preferred because inform request consumes more memory. There is a trade-off between reliability and resources.
As you see, with traps the receipt of the notification is not know by SNMP Agent. But with inform request if the notification do not reach to the SNMP Manager, after a period of time SNMP Agent sents the inform request again. It reaches in all events but the bandwidth usage increases.
There is a table below that can show the security models and the security levels of each SNMP version.
Until now, we have talked about SNMP generally. In the following articles, we will continue with SNMP configuration examples on various vendor devices, like Cisco, Juniper, Huawei and Nokia (Alcatel-Lucent).
Simple Network Management Protocol is mainly used for network device management and monitoring. With Simple Network Management Protocol and a Network Management System, we can monitor our routers, swicches and other devices in the network. We can also manage them, update them and do any other networking activitiy on these devices remotely.
There are two SNMP Protocol ports. These SNMP ports are UDP 161 and UDP 162. By default SNMP uses UDP port 161. UDP port 161 is used to send and receive SNMP requests. For SNMP Trap and Inform messages, UDP port 162 is used.
SNMP Traps are the messages with which SNMP Manager is informed about network condition. Traps is prefered mostly instead of Inform requests. Because they consume less resources.
We use traps if every notifications are not important and there is a resource shortage.
We use inform messages, if you want from SNMP Manager to get all the notifications.
SNMP v3 is the latest version of Simple Network Management Protocol.
Je veux apprendre le cours ccna
Hi Babacar, you can start with our self paced Cisco CCNA course.