- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
As we have talked about static routing and mentined before, the default administrative distace of Static routes is 1 for Cisco routers. It is the most trustful connection after directly connected networks. The administrative distance of the directly connected networks is 0. So, can we change the default administrative distance value of a static route? Yes. But how?
You can also check Cisco Static Routing Example
Static routes can be used in different roles in the networks. They can be used to teach a network to a network. Beside, they can also used as a backup connection for a destination. So, the static routes used for this purposes is called Floating Static Routes. Floating routes can be used with one more static routes or they can be used together with routing protocols. In both cases, floating static routes resides as a backup route. We can say that a floating route is a static route that has manuplated administrative distance value.
Floating static routes are the routes whose default administrative distance is changed manually with a higher admnistrative distance value. The aim of this higher administrative distance is to use this floating static route as a backup route. Because a floating route with an higher administrative distance value is not selectedas best path. Instead of it another route is selcted. And whenever this better path fails, then floating route is used as Best Path.
Firsly, let’s give an example for Floating Routes. Thisn about that, we are reaching a network through two different network. For such a situation, we can define two static routes. One of them is the real one and the other is backup floating static route. Here, we will not change the adminsitrative distance of the first static route. But we will change the administrative distance of the second static route.
As you can see below, there are two rotues to reach 30.30.30.0/24 network. One of the is the short way and the other one is the long way. Here, we will not change the default administrative distance of the first static route. So, the prefered static route will be this route. But, we will change the adminstartive distance of the second route as 5. By doing this, we configure a floating static route. If there is a failure in the first route, for example igf Router B becomes down, the second way will be selected through Router D and Router C that we have defined with floating static route.
To provide the full connectivity in this topology, we should add additional static routes. But here, for not to mix your mind, I willl not write these static routes.
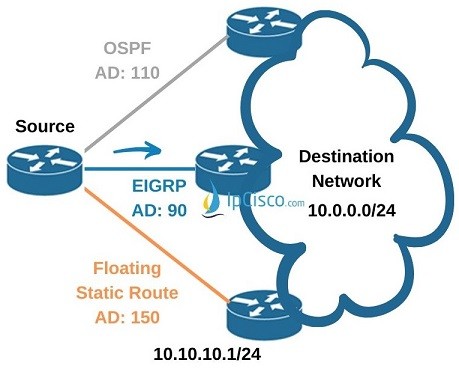
Let’s explain this with a scenario. Think about that we have three routes to a destination. One is learned by OSPF, the other is learned by EIGRP and the other is defined as static route. Normally, the admnistrative distances of these two routes are like below:
According to the best path algorithm of the routers, Static Route is selected as Best Path, and the traffic goes through this path. If it fails, EIGRP path is selected and then if this way also fails, OSPF path is selected.
To change this behaviour, we can define a Floating Static Route instead of this Static Route. For example, we can give an Administrative distance 150 to this floating static route and in this new situation, this route is not selected as Best Path. Instead, the routing protocol that has the lowest Administrative Distance is elected as Best Path. In our scenarios, this is EIGRP.
To configure Floating Static Route, we use the same command that we use in Static Route. Floating Static Routes are already Static Routes. The only difference is, with Floating Static Routes, we will give an extra Administrative Distance value to manuplate Route Selection.
In this scenario the destination network is 10.0.0.0/24. And our gateway is 10.10.10.1. And we will give 150 as Administrative Distance.
Router# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1 150
To check the Floating Static Route configuration we can use “show ip route static” and “show ip route 10.0.0.0” command.
Router # show ip route staticS 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0/0
Router # show ip route 10.0.0.0
Routing entry for 10.0.0.0/24
Known via “static”, distance 150, metric 0 (connected)
Routing Descriptor Blocks:* directly connected, via Ethernet0/0/0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
We can also check the Routing Table with “show ip route” command to check the selected Best Path.
You can find some of the default Administrative Distance values for Cisco below:
You can also check IPv6 Floating Static Routes Lesson.
Leave a Reply