- COURSES
- SPECIALS
- BLOG
- MEMBERS
- SHOP
- ABOUT
- ENROLL HERE
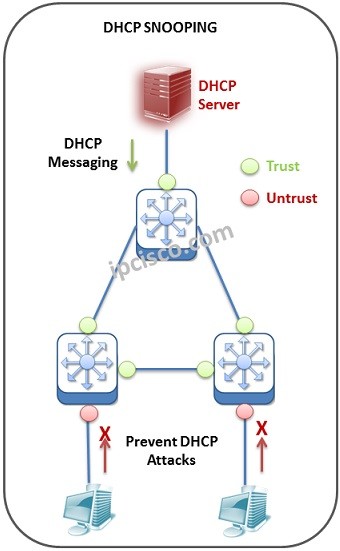
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is one of the most important protocols for our network. With DHCP we can configure IP configurations of our nodes in the network. This DHCP configurations can be done with various DHCP messages. But sometimes these messages can be used for some malicious attacks. So, what is DHCP Snooping meaning? DHCP Snooping is used on switches to detect such malicious attacks. Basically, this mechanism listens the DHCP messages of “untrusted” ports, records port and device information, according to the verification, it determines the harmful ones and prevent.
In this lesson, we will learn what is DHCP Snooping meaning? And in another lesson, we will configure DHCP Snooping on Cisco Packet Tracer.
Table of Contents
Many things! As you know, DHCP Server gives IP configurations to our network devices. Think about it, what if a malicious atttacker gives this IP addresses? If an attacker uses a DHCP software and take over your DHCP messaging, he/she can assign your IP addresses. He/She can do this by replying a DHCP Discover messages earlier than your real DHCP Server. He/she can give his/her IP address as a gateway for you. And then? Your all traffic o through his/her device. This is one of the way that a man-in-the-middle attack occurs.
A DHCP attacker can also manuplate your real DHCP Server’s pool. He/she can send a lot of DHCP Discover messages and get your IP addresses in DHCP Pool. Whenever your DHCP pool exhaust, IP configurations in the network can not be done.
DHCP Snooping is the inspector and a guardian of our network here. It is configured on switches. It Works as a firewall between DHCP Server and other part of the network. Here, DHCP Snooping tracks all the DHCP Discover and DHCP Offer messages coming from “untrusted” ports.
According to this Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) security system, there are two port types. These port types are:
First of all to enable this mechanism on a Cisco device, we shouk use “ip dchp snooping” command under the global configuration mode of a Cisco router or a Cisco switch.
Trusted ports are the ports that are set as verified at the beginning, This means that, any DHCP messages are accepted from this interface. To configure a Cisco device port as trusted, we use “ip dhcp snooping trust” command.
Untrusted ports are the ports that are set as unverified at the beginning. This means that, “be careful for the packets coming from this interface”.
At the beginning of the configuration, the required ports set as “untrusted”. This ports are generally user ports. Simply, we configure all the ports rather than DHCP Server in the network as “untrusted” with DHCP Snooping. Because, we would like to receive DHCP messages only form real DHCP Server of the network. Here, the ports connected to the DHCP Server, will be ”trusted” ports.
Another thing that we can d with DHCP Snooping is, limiting the DHCP Discover messages by “rate-limit”. This prevent our DHCP Pool from any exhaust. As we mentioned above, some attackers’ aim is directly the IP Pool of the DHCP Server.
DHCP Snooping fills a table named “DHCP Binding Table”. Accordig to this table, only the verified hosts are accepted to the network. Here, these entries are full of the devices connected to “untrusted” ports. There is no info about trusted ports in this “DHCP Binding Table”.
In the “DHCP Binding Table”, important information of the hosts are recorded. These information includes:
By default DHCP Snooping is not active. To use DHCP Snooping, we should enable it. By the way, DHCP Snooping can be enabled either for a single VLAN or for a range of VLANs.
After the configuration of this mechanism on a Cisco device, you can check the configuration with the below show commands:
As we mentioned above, DHCP Snooping checks the untursted ports and their DHCP behaviours. Even if itdetects aa malicious behaviour, in other words any DHCP violation, the message is dropped and a message logged. These mesages can be like below:
This message shows that a DHCP Offer message come from an untursted port. This is a very serious problem. In other words, somebody are trying to be your new DHCP Server, a rogue DHCP Server.
This message shows any MAC mismatch between Source of Ethernet frame and Client. In other words, there is a mmismatch in “DHCP Binding Table”.
DHCP Option 82 is an additional security mechanism over DHCP Snooping which is also known as ”DHCP Relay Agent Information”.
There are various DHCP Options an done of them is DHCP Option 82. With this option a client can send a DHCP message to DHCP Server in another network. This is done adding a DHCP Option 82 field to the header by DHCP Relay Agent.
This Option has created with RFC 3046. In another lesson, we will detailly talk about it.
DHCP Snooping protect against common dhcp attacks in networking. These attacks are DHCP Spoofing Attack and DHCP Starvation Attack. Now, let’s focus on how does it prenvents networks againsts such network attacks.
DHCP Spoofing attack is a Man-in-th-Middle attack with which attacker locate itself between DHCP Server and Victim. By doing this, attacker responds DHCP Requests and shows itself as a trustful DHCP resource. If you use DHCP Snooping, you can protect your system towards DHCP spoofing attacks.
DHCP Starvation attack is another DHCP attack type. DHCP Starvation attack is basically targets a DHCP Server with too much DHCP Requests. DHCP Server responds this requests with ip address assignements and this results in ip address pool exhaust. To prevent a network towards DHCP Starvation attack, you can use DHCP snooping configuration.
a) trusted
b) secured
c) unsecured
d) untrusted
a) trusted
d) untrusted
a) True
b) False
a) True
b) False
a) True
b) False
Answers: 1)a,d 2)a 3)b 4)b 5)a
Leave a Reply